Immunogenic potential and neutralizing ability of a heterologous version of the most abundant three-finger toxin from the coral snake Micrurus mipartitus
- PMID: 39628669
- PMCID: PMC11614397
- DOI: 10.1590/1678-9199-JVATITD-2023-0074
Immunogenic potential and neutralizing ability of a heterologous version of the most abundant three-finger toxin from the coral snake Micrurus mipartitus
Abstract
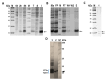
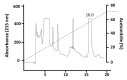
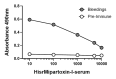
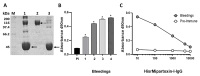
Background: Micrurus mipartitus is a coral snake of public health concern in Colombia. Its venom is mainly composed of three-finger toxins (3FTxs), Mipartoxin-1 being the most abundant protein partially responsible for its lethal effect. In this work, we present the production of Mipartoxin-1 in a recombinant form and evaluate its immunogenic potential. Methods: A genetic construct HisrMipartoxin-1 was cloned into the pET28a vector and heterologous expression was obtained in E. coli BL21 (DE3). The recombinant HisrMipartoxin-1 protein was extracted from inclusion bodies, refolded in vitro, and isolated by affinity and RP-HPLC chromatography. The lethal effect of HisrMipartoxin-1 was tested, and antibodies against HisrMipartoxin-1 were produced by immunization in rabbits. The antibody titers were monitored by an ELISA test. The neutralizing ability of the antibodies, against the lethal effect of native toxins and M. mipartitus venom, was also assessed. Results: HisrMipartoxin-1 was detected on SDS-PAGE, with a molecular mass of around 11 kDa. The retention time was 16.0 minutes. HisrMipartoxin-1 did not exhibit lethality in mice; however, antibodies against HisrMipartoxin-1 recognized the native toxin, the whole venom of M. mipartitus, and a 3FTx from another species within the Micrurus genus. Furthermore, antibodies against HisrMipartoxin-1 completely neutralized the lethal effect of native Mipartoxin-1 in mice but not M. mipartitus whole venom. Conclusion: These findings indicate that HisrMipartoxin-1 might be used as an immunogen to develop anticoral antivenoms or complement them. This work is the first report of the heterologous expression of 3FTx from M. mipartitus.
Keywords: Antibodies; Coral snake antivenoms; Micrurus mipartitus; Mipartoxin-1; Recombinant protein; Three-finger toxin.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors have declared that no conflicts of interest exist regarding this manuscript.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Anti-Neurotoxins from Micrurus mipartitus in the Development of Coral Snake Antivenoms.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Apr 9;14(4):265. doi: 10.3390/toxins14040265. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35448874 Free PMC article.
-
Novel three-finger toxins from Micrurus dumerilii and Micrurus mipartitus coral snake venoms: Phylogenetic relationships and characterization of Clarkitoxin-I-Mdum.Toxicon. 2019 Dec;170:85-93. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2019.09.017. Epub 2019 Sep 23. Toxicon. 2019. PMID: 31557485
-
Heterologous Expression and Immunogenic Potential of the Most Abundant Phospholipase A2 from Coral Snake Micrurus dumerilii to Develop Antivenoms.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Nov 24;14(12):825. doi: 10.3390/toxins14120825. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36548722 Free PMC article.
-
In-depth immunorecognition and neutralization analyses of Micrurus mipartitus and M. dumerilii venoms and toxins by a commercial antivenom.Biochimie. 2024 Jan;216:120-125. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2023.10.009. Epub 2023 Oct 14. Biochimie. 2024. PMID: 37844754
-
Immunological cross-recognition and neutralization studies of Micrurus mipartitus and Micrurus dumerilii venoms by two therapeutic equine antivenoms.Biologicals. 2020 Nov;68:40-45. doi: 10.1016/j.biologicals.2020.08.011. Epub 2020 Sep 11. Biologicals. 2020. PMID: 32928631
References
-
- World Health Assembly Addressing the Burden of Snakebite Envenoming. 2018;17
-
- Gutiérrez JM, Calvete JJ, Habib AG, Harrison RA, Williams DJ, Warrell DA. Snakebite envenoming. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17063. - PubMed
-
- Instituto Nacional de Salud . Portal SIVIGILA. Accidente Ofídico. Período Epidemiológico XIII. Colombia: 2022.
-
- Roze JA. Coral Snakes of the Americas: Biology, Identification, and Venoms. Krieger Publishing Company; Malabar, FL, United States: 1996.
-
- Otero-Patiño R. In: Clinical Toxinology. Gopalakrishnakone P, Faiz SMA, Gnanathasan CA, Habib AG, Fernando R, Yang C-C, editors. Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Springer; 2014. Snake Bites in Colombia; pp. 1–42.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
