Mechanical loading reveals an intrinsic cardiomyocyte stiffness contribution to diastolic dysfunction in murine cardiometabolic disease
- PMID: 39629708
- PMCID: PMC11649524
- DOI: 10.1113/JP286437
Mechanical loading reveals an intrinsic cardiomyocyte stiffness contribution to diastolic dysfunction in murine cardiometabolic disease
Abstract
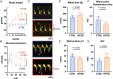
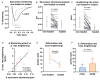
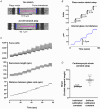
Cardiometabolic syndromes including diabetes and obesity are associated with occurrence of heart failure with diastolic dysfunction. There are no specific treatments for diastolic dysfunction, and therapies to manage symptoms have limited efficacy. Understanding of the cardiomyocyte origins of diastolic dysfunction is an important priority to identify new therapeutics. The investigative goal was to experimentally define in vitro stiffness properties of isolated cardiomyocytes derived from rodent hearts exhibiting diastolic dysfunction in vivo in response to dietary induction of cardiometabolic disease. Male mice fed a high fat/sugar diet (HFSD vs. control) exhibited diastolic dysfunction (echo E/e' Doppler ratio). Intact paced cardiomyocytes were functionally investigated in three conditions: non-loaded, loaded and stretched. Mean stiffness of HFSD cardiomyocytes was 70% higher than control. E/e' for the HFSD hearts was elevated by 35%. A significant relationship was identified between in vitro cardiomyocyte stiffness and in vivo dysfunction severity. With conversion from the non-loaded to loaded condition, the decrement in maximal sarcomere lengthening rate was more accentuated in HFSD cardiomyocytes (vs. control). With stretch, the Ca2+ transient decay time course was prolonged. With increased pacing, cardiomyocyte stiffness was elevated, yet diastolic Ca2+ elevation was attenuated. Our findings show unequivocally that cardiomyocyte mechanical dysfunction cannot be detected by analysis of non-loaded shortening. Collectively, these findings demonstrate that a component of cardiac diastolic dysfunction in cardiometabolic disease is derived from cardiomyocyte stiffness. Differential responses to load, stretch and pacing suggest that a previously undescribed alteration in myofilament-Ca2+ interaction contributes to intrinsic cardiomyocyte stiffness in cardiometabolic disease. KEY POINTS: Understanding cardiomyocyte stiffness components is an important priority for identifying new therapeutics for diastolic dysfunction, a key feature of cardiometabolic disease. In this study cardiac function was measured in vivo (echocardiography) for mice fed a high-fat/sugar diet (HFSD, ≥25 weeks). Performance of intact isolated cardiomyocytes derived from the same hearts was measured during pacing under non-loaded, loaded and stretched conditions in vitro. Calibrated cardiomyocyte stretches demonstrated that stiffness (stress/strain) was elevated in HFSD cardiomyocytes in vitro and correlated with diastolic dysfunction (E/e') in vivo. HFSD cardiomyocyte Ca2+ transient decay was prolonged in response to stretch. Stiffness was accentuated with pacing increase while the elevation in diastolic Ca2+ was attenuated. Data show unequivocally that cardiomyocyte mechanical dysfunction cannot be detected by analysis of non-loaded shortening. These findings suggest that stretch-dependent augmentation of the myofilament-Ca2+ response during diastole partially underlies elevated cardiomyocyte stiffness and diastolic dysfunction of hearts of animals with cardiometabolic disease.
Keywords: Ca2+ myofilament interaction; cardiometabolic disease; cardiomyocyte; diastolic dysfunction; relaxation; stiffness.
© 2024 The Author(s). The Journal of Physiology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of The Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Update of
-
Mechanical loading reveals an intrinsic cardiomyocyte stiffness contribution to diastolic dysfunction in murine cardiometabolic disease.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 12:2024.02.21.581448. doi: 10.1101/2024.02.21.581448. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: J Physiol. 2024 Dec;602(24):6705-6727. doi: 10.1113/JP286437. PMID: 38659933 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Abdellatif, M. , Trummer‐Herbst, V. , Koser, F. , Durand, S. , Adão, R. , Vasques‐Nóvoa, F. , Freundt, J. K. , Voglhuber, J. , Pricolo, M.‐R. , Kasa, M. , Türk, C. , Aprahamian, F. , Herrero‐Galán, E. , Hofer, S. J. , Pendl, T. , Rech, L. , Kargl, J. , Anto‐Michel, N. , Ljubojevic‐Holzer, S. , …, Sedej, S (2021). Nicotinamide for the treatment of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Science Translational Medicine, 13(580), eabd7064. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aurigemma, G. P. , Zile, M. R. , & Gaasch, W. H (2006). Contractile behavior of the left ventricle in diastolic heart failure. Circulation, 113(2), 296–304. - PubMed
-
- Borlaug, B. A. , Melenovsky, V. , Redfield, M. M. , Kessler, K. , Chang, H.‐J. , Abraham, T. P. , & Kass, D. A (2007). Impact of arterial load and loading sequence on left ventricular tissue velocities in humans. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 50(16), 1570–1577. - PubMed
-
- Bub, G. , Camelliti, P. , Bollensdorff, C. , Stuckey, D. J. , Picton, G. , Burton, R. A. B. , Clarke, K. , & Kohl, P (2010). Measurement and analysis of sarcomere length in rat cardiomyocytes in situ and in vitro. American Journal of Physiology‐Heart and Circulatory Physiology, 298(5), H1616–H1625. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

