Ampelopsis japonica enhances the effect of radiotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 39630250
- PMCID: PMC12119655
- DOI: 10.1007/s00066-024-02322-7
Ampelopsis japonica enhances the effect of radiotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: Radiotherapy is widely used in the clinical treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); however, its effectiveness often proves unsatisfactory. Ampelopsis japonica (AJ) is a traditional Chinese herb with anti-inflammatory and anticancer activities. However, whether AJ could enhance the effect of radiotherapy in NSCLC needs to be further explored.
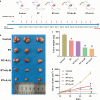
Methods: In vivo, BALB/c nude mice were used for a xenograft tumor model to explore whether AJ could enhance the effect of radiation therapy (RT) in NSCLC. In vitro, human NSCLC cell lines HCC827 and H1299 were used to explore the effect of AJ on the cell proliferation and apoptosis of RT-treated NSCLC. Moreover, bioinformatic analysis was performed to analyze the signaling pathways regulated by AJ.
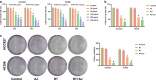
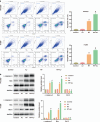
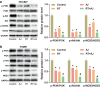
Results: Ampelopsis japonica enhanced the inhibitory effect of RT on NSCLC tumor growth in vivo. Simultaneously, AJ further enhanced the inhibitory effect of RT on NSCLC proliferation and the promoting effect of RT on NSCLC apoptosis. Bioinformatic analysis showed that AJ regulated the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. We confirmed that AJ decreased the protein levels of the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. Furthermore, the combination of AJ and RT suppressed activation of the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway.
Conclusion: Ampelopsis japonica augmented the inhibitory impact of RT on NSCLC cell proliferation and tumor growth by suppressing the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway.
Keywords: Tumor growth; Apoptosis; Medicine, Chinese traditional; PI3K-Akt signaling pathway; Radiation therapy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: Z. Liu, P. Cui, Q. Wu, and X. Ji declare that they have no competing interests. Ethical standards: The experimental protocol of our study was performed in accordance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and approved by the Ethics Committee of Shanxi Province Cancer Hospital Central Hospital (GPTAP001). Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Figures

Similar articles
-
SIRT6 through PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway to enhance radiosensitivity of non-Small cell lung cancer and inhibit tumor progression.IUBMB Life. 2021 Sep;73(9):1092-1102. doi: 10.1002/iub.2511. Epub 2021 Jun 4. IUBMB Life. 2021. PMID: 34033225
-
Agrimonia pilosa Extract suppresses NSCLC growth through regulating PI3K/AKT/Bcl-2 pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Jun 26;350:119892. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.119892. Epub 2025 Apr 29. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40311718
-
Response of non-small cell lung cancer cells to the inhibitors of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt- and MAPK kinase 4/c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase pathways: an effective therapeutic strategy for lung cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2005 Aug 15;11(16):6065-74. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0009. Clin Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16115952
-
Apoptosis induced by the methanol extract of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge in non-small cell lung cancer through PTEN-mediated inhibition of PI3K/Akt pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 Mar 22;200:107-116. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.12.051. Epub 2017 Jan 12. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28088493
-
The inhibitory effects of modified HSJZ decoction on NSCLC by regulating regulatory T cells via downregulation of EZH2 and PI3K/AKT pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 May 28;348:119802. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.119802. Epub 2025 Apr 15. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40245962
References
-
- Sung H et al (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71(3):209–249 - PubMed
-
- Harðardottir H et al (2022) Advances in lung cancer diagnosis and treatment—a review. Laeknabladid 108(1):17–29 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

