Evaluation of circulating tumor DNA as a prognostic and predictive biomarker in BRAF V600E mutated colorectal cancer-results from the FIRE-4.5 study
- PMID: 39630848
- PMCID: PMC11793001
- DOI: 10.1002/1878-0261.13778
Evaluation of circulating tumor DNA as a prognostic and predictive biomarker in BRAF V600E mutated colorectal cancer-results from the FIRE-4.5 study
Abstract
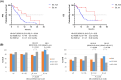
The randomized FIRE-4.5 (AIO KRK0116) trial compared first-line therapy with FOLFOXIRI (folinic acid, fluorouracil, oxaliplatin, and irinotecan) plus either cetuximab or bevacizumab in B-Raf proto-oncogene, serine/threonine kinase (BRAF) V600E-mutant metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) patients. This study was accompanied by a prospective translational project analyzing cell-free circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) in plasma to test whether ctDNA analysis may help to guide clinical treatment decision making. FIRE-4.5 included mCRC patients with BRAF V600E mutation detected by tissue-based analyses. Liquid biopsies (LBs) were collected at baseline (pre-treatment) and during therapy. Digital droplet PCR (ddPCR) technology was applied for determination of BRAF mutations and the in vitro diagnostics (IVD)-certified ONCOBEAM RAS procedure for analysis of RAS mutations. The BRAF V600E variants in ctDNA were analyzable in 66 patients at start of the therapy, at baseline. No BRAF V600E mutations were detected in 26% (17/66) of patients and was associated with a significantly longer progression-free survival (PFS: 13.2 vs 6.5 months; HR 0.47; P = 0.014) and overall survival (OS: 36.8 vs 13.2 months; HR 0.35; P = 0.02) as compared to ctDNA mutant patients. Patients with detectable BRAF mutations showed a clear superiority of FOLFOXIRI plus bevacizumab with regard to PFS (10.4 vs 5.7 months; HR 0.4; P = 0.009) and OS (16.6 vs 11.6 months; HR 0.5; P = 0.15), while this was not the case for BRAF wild-type patients. Follow-up LBs were obtained from 51 patients. Patients converting from BRAF V600E mutant to a BRAF V600 wild-type status (36%, N = 18) had a superior PFS (8.6 vs 2.3 months; P = 0.0002) and OS (17.4 vs 5.1 months; P < 0.0001) compared to patients with stable or increased mutational allele frequency (12%, N = 6). Those patients also achieved a significantly greater disease control rate (89% vs 20%; P = 0.008). In conclusion, LB evaluating ctDNA is informative and may help to guide treatment in patients with BRAF V600E-mutated mCRC.
Keywords: FOLFOXIRI; bevacizumab; cetuximab; circulating tumor DNA; liquid biopsy; mutational load.
© 2024 The Author(s). Molecular Oncology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
SKS, WS, TM, RS, SH declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram I, Parkin DM, Piñeros M, Znaor A, et al. Cancer statistics for the year 2020: an overview. Int J Cancer. 2021;149:778–789. - PubMed
-
- Douillard J‐Y, Oliner KS, Siena S, Tabernero J, Burkes R, Barugel M, et al. Panitumumab‐FOLFOX4 treatment and RAS mutations in colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:1023–1034. - PubMed
-
- Schmoll HJ, van Cutsem E, Stein A, Valentini V, Glimelius B, Haustermans K, et al. ESMO consensus guidelines for management of patients with colon and rectal cancer. A personalized approach to clinical decision making. Ann Oncol. 2012;23:2479–2516. - PubMed
-
- Yoshino T, Arnold D, Taniguchi H, Pentheroudakis G, Yamazaki K, Xu R‐H, et al. Pan‐Asian adapted ESMO consensus guidelines for the management of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: a JSMO‐ESMO initiative endorsed by CSCO, KACO, MOS, SSO and TOS. Ann Oncol. 2018;29:44–70. - PubMed
-
- Cervantes A, Adam R, Roselló S, Arnold D, Normanno N, Taïeb J, et al. Metastatic colorectal cancer: ESMO clinical practice guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow‐up. Ann Oncol. 2023;34:10–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

