Alternative splicing of Clock transcript mediates the response of circadian clocks to temperature changes
- PMID: 39630861
- PMCID: PMC11648895
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2410680121
Alternative splicing of Clock transcript mediates the response of circadian clocks to temperature changes
Abstract
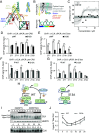
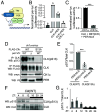
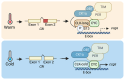
Circadian clocks respond to temperature changes over the calendar year, allowing organisms to adjust their daily biological rhythms to optimize health and fitness. In Drosophila, seasonal adaptations are regulated by temperature-sensitive alternative splicing (AS) of period (per) and timeless (tim) genes that encode key transcriptional repressors of clock gene expression. Although Clock (Clk) gene encodes the critical activator of circadian gene expression, AS of its transcripts and its potential role in temperature regulation of clock function have not been explored. Here, we observed that Clk transcripts undergo temperature-sensitive AS. Specifically, cold temperature leads to the production of an alternative Clk transcript, hereinafter termed Clk-cold, which encodes a CLK isoform with an in-frame deletion of four amino acids proximal to the DNA binding domain. Notably, serine 13 (S13), which we found to be a CK1α-dependent phosphorylation site, is deleted in CLK-cold protein. We demonstrated that upon phosphorylation at CLK(S13), CLK-DNA interaction is reduced, thus decreasing transcriptional activity of CLK. This is in agreement with our findings that CLK occupancy at clock genes and transcriptional output are elevated at cold temperature likely due to higher amounts of CLK-cold isoforms that lack S13 residue. Finally, we showed that PER promotes CK1α-dependent phosphorylation of CLK(S13), supporting kinase-scaffolding role of repressor proteins as a conserved feature in the regulation of eukaryotic circadian clocks. This study provides insights into the complex collaboration between AS and phospho-regulation in shaping temperature responses of the circadian clock.
Keywords: alternative splicing; circadian rhythm; phosphorylation; post-translational modification; temperature.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
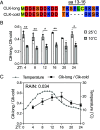
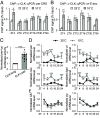
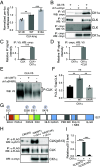
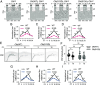

Update of
-
Alternative splicing of clock transcript mediates the response of circadian clocks to temperature changes.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 12:2024.05.10.593646. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.10.593646. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Dec 10;121(50):e2410680121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2410680121. PMID: 38766142 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Patke A., Young M. W., Axelrod S., Molecular mechanisms and physiological importance of circadian rhythms. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 21, 67–84 (2020). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK124068/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56DK124068/HHS | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK)
- R25 GM116690/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK124068/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK124068/HHS | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

