4'-Demethylpodophyllotoxin functions as a mechanism-driven therapy by targeting the PI3K-AKT pathway in Colorectal cancer
- PMID: 39631206
- PMCID: PMC11663980
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tranon.2024.102199
4'-Demethylpodophyllotoxin functions as a mechanism-driven therapy by targeting the PI3K-AKT pathway in Colorectal cancer
Abstract
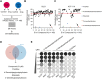
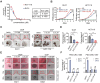
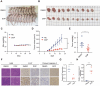
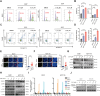
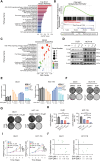
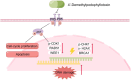
The treatment of colorectal cancer (CRC) poses significant challenges in terms of drug resistance and poor prognosis, necessitating the exploration of effective therapeutic strategies. In this study, high-throughput drug screening was utilized to identify Chinese herbal medicines with notable therapeutic effects on CRC. Among the compounds identified, 4'-demethylpodophyllotoxin (DOP), a derivative of podophyllotoxin, emerged as a potent anti-cancer compound. DOP exhibited time- and dose-dependent growth inhibition on CRC cell lines and tumor organoids derived from patients. RNA-seq revealed that DOP activated the PI3K-AKT pathway, leading to tumor cell apoptosis and cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase. Additionally, DOP induced DNA damage in CRC cells. To further validate its therapeutic efficacy in CRC, the DLD1-derived xenograft model demonstrated that DOP effectively suppressed CRC growth in vivo. In conclusion, these findings highlight the significant therapeutic potential of DOP as an anti-tumor drug for treating CRC, thereby opening new avenues for investigating Podophyllotoxin derivatives in this specific field.
Keywords: 4′-Demethylpodophyllotoxin; Chemoresistance; Colorectal cancer; PI3K-AKT pathway.
Copyright © 2024. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Dekker E., Tanis P.J., Vleugels J.L.A., Kasi P.M., Wallace M.B. Colorectal cancer. Lancet. 2019;394(10207):1467–1480. - PubMed
-
- Biller L.H., Schrag D. Diagnosis and treatment of metastatic Colorectal cancer: a review. JAMa. 2021;325(7):669–685. - PubMed
-
- Yang H., Yue G.G.L., Leung P.C., Wong C.K., Lau C.B.S. A review on the molecular mechanisms, the therapeutic treatment including the potential of herbs and natural products, and target prediction of obesity-associated colorectal cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2022;175 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

