An efficient measure for the isolation of chenodeoxycholic acid from chicken biles using enzyme-assisted extraction and macroporous resins refining
- PMID: 39631279
- PMCID: PMC11665364
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104573
An efficient measure for the isolation of chenodeoxycholic acid from chicken biles using enzyme-assisted extraction and macroporous resins refining
Abstract
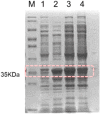
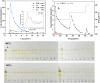
Chicken bile is a by-product of chicken processing, rich in chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA), an active pharmaceutical raw material. In this study, a green measure for the extraction and purification of CDCA from chicken biles by enzymatic hydrolysis and macroporous resins refining was established. For the assisted extraction of CDCA, the active bile salt hydrolase (BSH) from Bifidobacterium was heterologously expressed and applied, its activities on GCDCA and TCDCA were 4.96 ± 0.32 U/mg and 3.07 ± 0.031 U/mg and optimal catalytic conditions for the extraction of CDCA were determined as 0.04 g/g of the enzyme dosage, pH 5.0 and 38 °C. Through validation of the conditions, the yield of CDCA was up to 5.32 %, which was equivalent to that by saponification method. In order to further refine CDCA from the extract obtained by enzyme-assisted extraction, a more preferable resin, AB-8 was selected for the purification of CDCA, which had a good adsorption capacity of 61.06 ± 0.57 mg/g for CDCA. Besides, the obtained CDCA extract was purified through AB-8 resin, the purity of CDCA was improved from 51.7 % to 91.4 % and the recovery yield of CDCA was 87.8 %. The advantages of energy conservation, time saving, economy and environmental friendliness make the measure using enzyme-assisted extraction and macroporous resins refining a promising candidate for isolation of CDCA from chicken bile.
Keywords: Adsorption; Bile salt hydrolase; Chenodeoxycholic acid; Macroporous resin; Purification.
Copyright © 2024. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Aljeboree A.M., Alshirifi A.N., Alkaim A.F. Kinetics and equilibrium study for the adsorption of textile dyes on coconut shell activated carbon. Arab. J. Chem. 2017;10:S3381–S3393.
-
- Chang X.L., Wang D., Chen B.Y., Feng Y.M., Wen S.H., Zhan P.Y. Adsorption and desorption properties of macroporous resins for anthocyanins from the calyx extract of roselle (Hibiscus sabdariffa L.) J. Agr. Food Chem. 2012;60:2368–2376. - PubMed
-
- Corpechot C., Carrat F., Bonnand A.M., Poupon R.E., Poupon R. The effect of ursodeoxycholic acid therapy on liver fibrosis progression in primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2000;32:1196–1199. - PubMed
-
- Danzinger R.G., Hofmann A.F., Schoenfield L.J., Thistle J.L. Dissolution of cholesterol gallstones by chenodeoxycholic acid. N. Engl. J. Med. 1972;286:1–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

