Expression and delivery of HA1-M2e antigen using an innovative attenuated Salmonella-mediated delivery system confers promising protection against H9N2 avian influenza challenge
- PMID: 39631285
- PMCID: PMC11665344
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104602
Expression and delivery of HA1-M2e antigen using an innovative attenuated Salmonella-mediated delivery system confers promising protection against H9N2 avian influenza challenge
Abstract
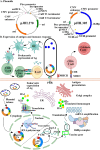
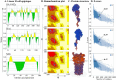
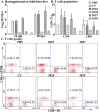
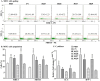
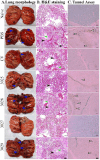
This study explores a dual expression vector system for delivering prokaryotic and eukaryotic antigens to improve conventional vaccination strategies. To enhance immune protection against H9N2 avian influenza virus (AIV), which threatens poultry and humans, we used the previously constructed pJHL270 and pJHL305 plasmids with the Ptrc and CMV promoters to stimulate MHC class II and I responses through exogenous and endogenous antigenic presentation. Salmonella Gallinarum (SG), a delivery vector, was engineered to have defective lipopolysaccharide structures through lon, pagL, and rfaL deletion. It demonstrated a safety profile with lower induction of inflammatory cytokines than the wild-type strain. Bioinformatics tools predicted that the HA1 and M2e sequences, which were designed as consensus sequences of South Korean strains (2000-2021), would have high antigenicity and favorable structures. In vitro expression of the vaccine constructs was validated by western blotting. Birds immunized with attenuated SG harboring pJHL270 (JOL3025) or pJHL305 (JOL3027) containing HA-M2e showed significant increases in serum IgY and mucosal IgA antibodies, indicating strong humoral and mucosal immune responses, comparable with inactivated commercial vaccine. Post-immunization, we found a substantial rise in the hemagglutination inhibition titer, suggesting effective prevention of viral attachment and robust cell-mediated immunity, with a 1.96-fold and 2.80-fold increase in CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, respectively, for JOL3025 and a 1.75-fold and 2.49-fold increase for JOL3027. Furthermore, MHC class I and II expression increased 1.35-fold and 1.63-fold, for JOL3025, and 1.61-fold and 1.68-fold, respectively, for JOL3027. The IL-4 and IFN-γ levels were elevated, indicating a balanced Th-1 and Th-2 response. Post-challenge, birds immunized with vaccine candidates or the commercial vaccine exhibited minimal to no clinical signs, reduced lesions, lower lung viral titers, and negligible impacts on egg production compared to controls. In conclusion, both plasmids successfully delivered HA1-M2e immunogens through the engineered SG strains, eliciting strong humoral, mucosal, and cell-mediated immune responses and co-stimulating MHC class I and II antigen presentation pathways to provide effective protection against H9N2 AIV with minimal adverse effects.
Keywords: Cell-Mediated response; Dual expression system; H9N2; Salmonella; Viral titer.
Copyright © 2024. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

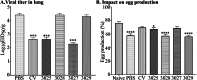
References
-
- Aganja R.P., Senevirathne A., Sivasankar C., Lee J.H. Salmonella-Delivered COBRA-HA1 antigen derived from H1N1 hemagglutinin sequences elicits broad-spectrum protection against influenza A subtypes. Engineering. 2024;32:41–56.
-
- Belshe R.B., Gruber W.C., Mendelman P.M., Mehta H.B., Mahmood K., Reisinger K., Treanor J., Zangwill K., Hayden F.G., Bernstein D.I., Kotloff K., King J., Piedra P.A., Block S.L., Yan L., Wolff M. Correlates of immune protection induced by live, attenuated, cold-adapted, trivalent, intranasal influenza virus vaccine. J. Infect. Dis. 2000;181(3):1133–1137. doi: 10.1086/315323. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

