Associations of the Expression Levels and Risk Variants of CDKN2B-AS1 Long Noncoding RNA With the Susceptibility and Progression of Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 39632396
- PMCID: PMC11617473
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.70264
Associations of the Expression Levels and Risk Variants of CDKN2B-AS1 Long Noncoding RNA With the Susceptibility and Progression of Prostate Cancer
Abstract
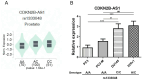
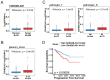
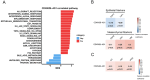
Genetic variants of deregulated long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been implicated in tumorigenesis, cancer progression and cancer recurrence. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of the lncRNA cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2B antisense RNA 1 (CDKN2B-AS1) have been associated with the risk and progression of various cancers; however, their role in prostate cancer (PCa) remains underexplored. In this case-control study, we investigated the associations of CDKN2B-AS1 expression levels and variants with PCa risk and progression. For this, five SNPs of CDKN2B-AS1-rs564398, rs1333048, rs1537373, rs2151280 and rs8181047-were genotyped using a TaqMan allelic discrimination assay; data were collected from 695 patients with PCa and 695 healthy controls. Our findings revealed that, under a dominant model, patients with PCa carrying at least one minor C allele of rs1333048 exhibited an increased risk of developing tumours with high Gleason grades; this risk was particularly high in patients without biochemical recurrence. Data from the Genotype-Tissue Expression database indicated upregulated CDKN2B-AS1 expression in the prostates of individuals carrying the polymorphic C allele of rs1333048. Genotype screening of rs1333048 in PCa cell lines showed that cells with at least one minor C allele had higher CDKN2B-AS1 levels than those with the AA genotype. Furthermore, data from The Cancer Genome Atlas indicated that higher CDKN2B-AS1 levels in PCa tissues were correlated with larger tumour sizes (T3 + T4), more lymph node metastasis (N1), higher Gleason scores and shorter progression-free survival. In conclusion, the polymorphic variants of CDKN2B-AS1 at rs1333048 may modulate CDKN2B-AS1 expression, thus accelerating PCa progression.
Keywords: cancer progression; cancer susceptibility; cyclin‐dependent kinase inhibitor 2B antisense RNA 1; long noncoding RNA; prostate cancer; single‐nucleotide polymorphism.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

