Microfluidic Nanoparticle Separation for Precision Medicine
- PMID: 39632600
- PMCID: PMC11775552
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202411278
Microfluidic Nanoparticle Separation for Precision Medicine
Abstract
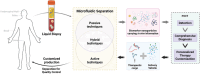
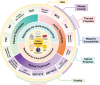
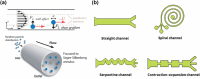
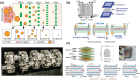
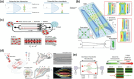
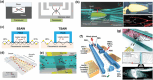
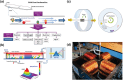
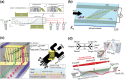
A deeper understanding of disease heterogeneity highlights the urgent need for precision medicine. Microfluidics, with its unique advantages, such as high adjustability, diverse material selection, low cost, high processing efficiency, and minimal sample requirements, presents an ideal platform for precision medicine applications. As nanoparticles, both of biological origin and for therapeutic purposes, become increasingly important in precision medicine, microfluidic nanoparticle separation proves particularly advantageous for handling valuable samples in personalized medicine. This technology not only enhances detection, diagnosis, monitoring, and treatment accuracy, but also reduces invasiveness in medical procedures. This review summarizes the fundamentals of microfluidic nanoparticle separation techniques for precision medicine, starting with an examination of nanoparticle properties essential for separation and the core principles that guide various microfluidic methods. It then explores passive, active, and hybrid separation techniques, detailing their principles, structures, and applications. Furthermore, the review highlights their contributions to advancements in liquid biopsy and nanomedicine. Finally, it addresses existing challenges and envisions future development spurred by emerging technologies such as advanced materials science, 3D printing, and artificial intelligence. These interdisciplinary collaborations are anticipated to propel the platformization of microfluidic separation techniques, significantly expanding their potential in precision medicine.
Keywords: microfluidic; nanomedicine; nanoparticles; precision medicine; separation.
© 2024 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Microfluidics for Nanomedicine Delivery.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2025 Feb 10;11(2):774-783. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.4c02052. Epub 2025 Jan 8. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2025. PMID: 39772433 Review.
-
[Research progress in the application of external field separation technology and microfluidic technology in the separation of micro/nanoscales].Se Pu. 2021 Nov;39(11):1157-1170. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2020.12032. Se Pu. 2021. PMID: 34677011 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Advancements in microfluidics for nanoparticle separation.Lab Chip. 2016 Dec 20;17(1):11-33. doi: 10.1039/c6lc01045h. Lab Chip. 2016. PMID: 27830852 Review.
-
Fabrication and Applications of Microfluidic Devices: A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 18;22(4):2011. doi: 10.3390/ijms22042011. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33670545 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Colorectal tumor-on-a-chip system: A 3D tool for precision onco-nanomedicine.Sci Adv. 2019 May 22;5(5):eaaw1317. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aaw1317. eCollection 2019 May. Sci Adv. 2019. PMID: 31131324 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mousa S. A., Bawa R., Audette G. F., The Road from Nanomedicine to Precision Medicine, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL: 2020.
-
- Hawgood S., Hook‐Barnard I. G., O'Brien T. C., Yamamoto K. R., Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 300ps17. - PubMed
-
- Chatzis L. G., Argyropoulou O., Panagiotopoulos K., Palla P., Tzioufas A. G., (Ed.: Bydon M.), Academic Press; 2024, pp. 173–194.
-
- Borrebaeck C. A. K., Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 199. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
