A Smart Nanomedicine Unleashes a Dual Assault of Glucose Starvation and Cuproptosis to Supercharge αPD-L1 Therapy
- PMID: 39632613
- PMCID: PMC11775525
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202411378
A Smart Nanomedicine Unleashes a Dual Assault of Glucose Starvation and Cuproptosis to Supercharge αPD-L1 Therapy
Abstract
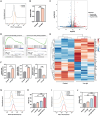
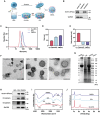
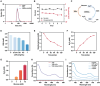
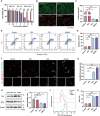
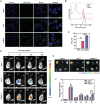
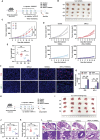
Combination therapy has become a promising strategy for promoting the outcomes of anti-programmed death ligand-1 (αPD-L1) therapy in lung cancer. Among all, emerging strategies targeting cancer metabolism have shown great potency in treating cancers with immunotherapy. Here, alteration in glucose and copper metabolisms is found to synergistically regulate PD-L1 expression in lung cancer cells. Thus, an intelligent biomimetic nano-delivery system is synthesized by camouflaging lung cancer cell membranes onto glucose oxidase-loaded Cu-LDHs (CMGCL) for cancer metabolism targeted interference. Such novel nanomedicine is able to induce lung cancer cell cuproptosis and PD-L1 upregulation significantly via self-amplified cascade reactions. Meanwhile, with a decent cancer cell membrane coating, CMGCL exhibited great biosafety, tumor-targeted efficiency and anti-tumor effects in LLC lung tumor-bearing mice models. Additionally, a combination of CMGCL can sensitize the therapeutic effects of αPD-L1, substantially promoting tumor inhibition in both subcutaneous and lung metastasis LLC-bearing mice models. Overall, these findings highlight the potential connections between glucose metabolism and cell cuproptosis, offering a promising approach for treating lung cancer by integrating starvation, cuproptosis, and immunotherapy.
Keywords: PD‐L1; biomimetic nanomedicine; cuproptosis; glucose metabolisms; lung cancer.
© 2024 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Vesely M. D., Zhang T., Chen L., Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 40, 45. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
