Yin Yang 1 and guanine quadruplexes protect dopaminergic neurons from cellular stress via transmissive dormancy
- PMID: 39632864
- PMCID: PMC11618784
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-54958-9
Yin Yang 1 and guanine quadruplexes protect dopaminergic neurons from cellular stress via transmissive dormancy
Abstract
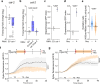
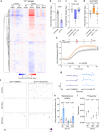
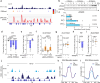
Neurons deploy diverse adaptive strategies to ensure survival and neurotransmission amid cellular stress. When these adaptive pathways are overwhelmed, functional impairment or neurodegeneration follows. Here we show that stressed neurons actively induce a state of transmissive dormancy as a protective measure. Extending observations of neurotrauma in C. elegans and mice, human dopaminergic neurons capable of surviving severe cellular challenges both decrease spontaneous activity and modulate dopamine homeostasis through the transcriptional regulator Yin Yang 1 (YY1). To bolster stress resilience and mitigate dopamine toxicity, YY1 increases expression of the vesicular monoamine transporter 2, vMAT2, while coordinately inhibiting dopamine synthesis through stabilization of a guanine quadruplex in intron 10 of tyrosine hydroxylase, TH. This dopaminergic stress response has the potential to cause circuit inactivation, yet safeguards neurons by minimizing the toxic accumulation of cytosolic dopamine and inducing a state of neuronal dormancy. In essence, neurons appear to actively prioritize viability over functionality.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Nikolaus, S., Antke, C. & Muller, H. W. In vivo imaging of synaptic function in the central nervous system: II. Mental and affective disorders. Behav. Brain Res.204, 32–66 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Kamenetz, F. et al. APP processing and synaptic function. Neuron37, 925–937 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Heo, J. Y. et al. Aberrant tonic inhibition of dopaminergic neuronal activity causes motor symptoms in animal models of Parkinson’s disease. Curr. Biol.30, 276–291.e279 (2020). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- GRFP 1000305318/National Science Foundation (NSF)
- F31 GM140620/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG076529/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 AG076529/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG061338/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

