Group 2 innate lymphoid cells are a non-redundant source of interleukin-5 required for development and function of murine B1 cells
- PMID: 39632879
- PMCID: PMC11618303
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-54780-3
Group 2 innate lymphoid cells are a non-redundant source of interleukin-5 required for development and function of murine B1 cells
Abstract
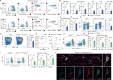
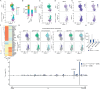
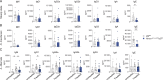
Tissue-resident immune cells, such as innate lymphoid cells, mediate protective or detrimental immune responses at barrier surfaces. Upon activation by stromal or epithelial cell-derived alarmins, group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) are a rapid source of type 2 cytokines, such as IL-5. However, due to the overlap in effector functions, it remains unresolved whether ILC2s are an essential component of the type 2 response or whether their function can be compensated by other cells, such as T cells. Here we show a non-redundant role of ILC2s in supporting the development and function of B1 cells. We demonstrate that B1 cells fail to develop properly in the absence of ILC2s and identify the IL-33 receptor on ILC2s as an essential cell-intrinsic regulator of IL-5 production. Further, conditional deletion of Il5 in ILC2s results in defective B1 cell development and immunoglobulin production. Consequently, B1 cells with phosphatidylcholine specific B cell receptor rearrangements are diminished in ILC2-deficient mice. Thus, our data establish an essential function of ILC2s in supporting B1 cells and antibody production at barrier surfaces.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: D.A. has contributed to scientific advisory boards at Pfizer, Takeda, FARE, and the KRF. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

