Eeg based smart emotion recognition using meta heuristic optimization and hybrid deep learning techniques
- PMID: 39632923
- PMCID: PMC11618626
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-80448-5
Eeg based smart emotion recognition using meta heuristic optimization and hybrid deep learning techniques
Abstract
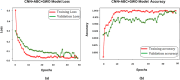
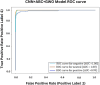
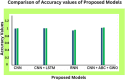
In the domain of passive brain-computer interface applications, the identification of emotions is both essential and formidable. Significant research has recently been undertaken on emotion identification with electroencephalogram (EEG) data. The aim of this project is to develop a system that can analyse an individual's EEG and differentiate among positive, neutral, and negative emotional states. The suggested methodology use Independent Component Analysis (ICA) to remove artefacts from Electromyogram (EMG) and Electrooculogram (EOG) in EEG channel recordings. Filtering techniques are employed to improve the quality of EEG data by segmenting it into alpha, beta, gamma, and theta frequency bands. Feature extraction is performed with a hybrid meta-heuristic optimisation technique, such as ABC-GWO. The Hybrid Artificial Bee Colony and Grey Wolf Optimiser are employed to extract optimised features from the selected dataset. Finally, comprehensive evaluations are conducted utilising DEAP and SEED, two publically accessible datasets. The CNN model attains an accuracy of approximately 97% on the SEED dataset and 98% on the DEAP dataset. The hybrid CNN-ABC-GWO model achieves an accuracy of approximately 99% on both datasets, with ABC-GWO employed for hyperparameter tuning and classification. The proposed model demonstrates an accuracy of around 99% on the SEED dataset and 100% on the DEAP dataset. The experimental findings are contrasted utilising a singular technique, a widely employed hybrid learning method, or the cutting-edge method; the proposed method enhances recognition performance.
Keywords: Artificial Bee colony; Convolutional neural network; Electroculogram; Electroencephalogram; Grey Wolf Optimizer; Hybrid learning methods.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




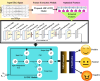
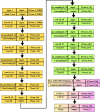

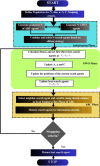
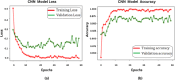



Similar articles
-
Cross-subject emotion recognition in brain-computer interface based on frequency band attention graph convolutional adversarial neural networks.J Neurosci Methods. 2024 Nov;411:110276. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2024.110276. Epub 2024 Sep 3. J Neurosci Methods. 2024. PMID: 39237038
-
EEG Emotion Recognition Based on 3D-CTransNet.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2024 Jul;2024:1-4. doi: 10.1109/EMBC53108.2024.10782401. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2024. PMID: 40031451
-
Enhancing EEG-Based Emotion Detection with Hybrid Models: Insights from DEAP Dataset Applications.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Mar 14;25(6):1827. doi: 10.3390/s25061827. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40292995 Free PMC article.
-
Hybrid hunt-based deep convolutional neural network for emotion recognition using EEG signals.Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2022 Sep;25(12):1311-1331. doi: 10.1080/10255842.2021.2007889. Epub 2022 Jan 31. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2022. PMID: 35098819
-
A natural evolution optimization based deep learning algorithm for neurological disorder classification.Biomed Mater Eng. 2020;31(2):73-94. doi: 10.3233/BME-201081. Biomed Mater Eng. 2020. PMID: 32474459 Review.
References
-
- Santiago, H. C., Ren, T. I. & Cavalcanti, G. D. Facial expression recognition based on motion estimation, 2016 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN) 1617–1624. (2016).
-
- Zhang, Z. et al. Multiscale adaptive local directional texture pattern for facial expression recognition. KSII Trans. Internet Inf. Syst.11 (2017).
-
- Sadoughi, N. & Busso, C. Speech-driven animation with meaningful behaviors. Speech Commun.110, 90–100 (2019).
-
- Malatesta, L., Asteriadis, S., Caridakis, G., Vasalou, A. & Karpouzis, K. Associating gesture expressivity with affective representations. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell.51, 124–135 (2016).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

