DGHSA: derivative graph-based hypergraph structure attack
- PMID: 39632934
- PMCID: PMC11618612
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-79824-y
DGHSA: derivative graph-based hypergraph structure attack
Abstract
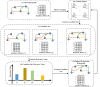
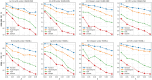
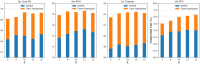
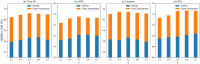
Hypergraph Neural Networks (HGNNs) have been significantly successful in higher-order tasks. However, recent study have shown that they are also vulnerable to adversarial attacks like Graph Neural Networks. Attackers fool HGNNs by modifying node links in hypergraphs. Existing adversarial attacks on HGNNs only consider feasibility in the targeted attack, and there is no discussion on the untargeted attack with higher practicality. To close this gap, we propose a derivative graph-based hypergraph attack, namely DGHSA, which focuses on reducing the global performance of HGNNs. Specifically, DGHSA consists of two models: candidate set generation and evaluation. The gradients of the incidence matrix are obtained by training HGNNs, and then the candidate set is obtained by modifying the hypergraph structure with the gradient rules. In the candidate set evaluation module, DGHSA uses the derivative graph metric to assess the impact of attacks on the similarity of candidate hypergraphs, and finally selects the candidate hypergraph with the worst node similarity as the optimal perturbation hypergraph. We have conducted extensive experiments on four commonly used datasets, and the results show that DGHSA can significantly degrade the performance of HGNNs on node classification tasks.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

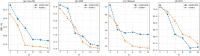
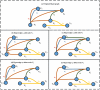
References
-
- Li, R. et al. Graph signal processing, graph neural network and graph learning on biological data: A systematic review. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng.16, 109–135. 10.1109/RBME.2021.3122522 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Zhang, R., Zhang, Y., Lu, C. & Li, X. Unsupervised graph embedding via adaptive graph learning. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell.45, 5329–5336. 10.1109/TPAMI.2022.3202158 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Ji, J., Jia, H., Ren, Y. & Lei, M. Supervised contrastive learning with structure inference for graph classification. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng.10, 1684–1695. 10.1109/TNSE.2022.3233479 (2023).
-
- Wang, K. et al. Minority-weighted graph neural network for imbalanced node classification in social networks of internet of people. IEEE Internet Things J.10, 330–340. 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3200964 (2023).
-
- Lyu, Z. et al. Knowledge enhanced graph neural networks for explainable recommendation. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng.35, 4954–4968 (2023).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

