High level of systemic immune inflammation index elevates delirium risk among patients in intensive care unit
- PMID: 39632969
- PMCID: PMC11618353
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-81559-9
High level of systemic immune inflammation index elevates delirium risk among patients in intensive care unit
Abstract
Evidence regarding the effect of systemic immune-inflammation index on delirium occurrence is limited. This study aimed to investigate the association between SII and delirium in intensive care unit (ICU) patients.
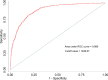
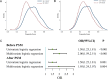
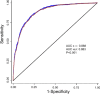
Methods: Information was extracted from Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care-IV. Four logistic regression model was established and incorporated with subgroup analysis and restricted cubic spline (RCS). The cutoff value of SII was acquired from receiver operator characteristic curve (ROC), and propensity score matching (PSM) was utilized to attenuate the confounding effect. Survival analysis was utilized to evaluate the relationship between SII and 30-day or 90-day all-cause mortality.
Results: Among the 7,518 participants, 1,685 cases of delirium occurred. Individuals in the highest quartile of SII exhibited a heightened delirium risk, with a significant multivariable-adjusted odds ratio (OR) of 3.12(2.24,4.33). Tendency analysis, subgroup analysis and PSM together confirmed the positive relationship. Results of Cox regression displayed the risk of both 30-day and 90-day mortality increased about 50% in the higher-SII group.
Conclusion: Higher levels of SII is positively associated with the occurrence of delirium and increased all-cause mortality risk.
Keywords: Delirium; Intensive care unit; Medical information mart for intensive care-IV; Systemic immune-inflammation index.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval: Ethics approval and consent to use MIMIC-IV database were approved by the Institutional Review Boards of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, and consent was obtained for the original data collection. Thus, the informed consent was waived by an Institutional Review Board of West China Hospital, Sichuan University, or by ethics committee.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

