How J-chain ensures the assembly of immunoglobulin IgM pentamers
- PMID: 39632981
- PMCID: PMC11729874
- DOI: 10.1038/s44318-024-00317-9
How J-chain ensures the assembly of immunoglobulin IgM pentamers
Abstract
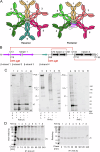
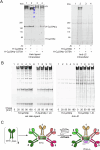
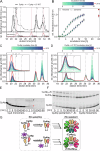
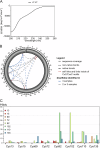
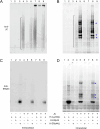
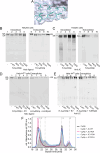
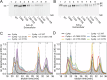
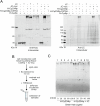
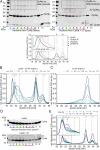
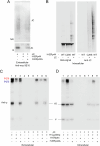
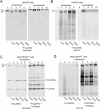
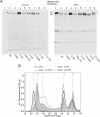
Polymeric IgM immunoglobulins have high avidity for antigen and complement, and dominate primary antibody responses. They are produced either as assemblies of six µ2L2 subunits (i.e., hexamers), or as pentamers of two µ2L2 subunits and an additional protein termed J-chain (JC), which allows transcytosis across epithelia. The molecular mechanism of IgM assembly with the desired stoichiometry remained unknown. Here, we show in vitro and in cellula that JC outcompetes the sixth IgM subunit during assembly. Before insertion into IgM, JC exists as an ensemble of largely unstructured, protease-sensitive species with heterogeneous, non-native disulfide bonds. The J-chain interacts with the hydrophobic β-sheets selectively exposed by nascent pentamers. Completion of an amyloid-like core triggers JC folding and drives disulfide rearrangements that covalently stabilize JC-containing pentamers. In cells, the quality control factor ERp44 surveys IgM assembly and prevents the secretion of aberrant conformers. This mechanism allows the efficient production of high-avidity IgM for systemic or mucosal immunity.
Keywords: Antibody Biogenesis; ERp44; Mucosal Immunity; Non-Native Disulfides; Protein Quality Control.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure and competing interests statement. The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

