Pharmacological blocking of neutrophil extracellular traps attenuates immunothrombosis and neuroinflammation in cerebral cavernous malformation
- PMID: 39632986
- PMCID: PMC11634782
- DOI: 10.1038/s44161-024-00577-y
Pharmacological blocking of neutrophil extracellular traps attenuates immunothrombosis and neuroinflammation in cerebral cavernous malformation
Abstract
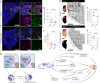
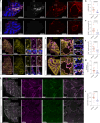
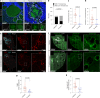
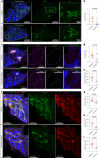
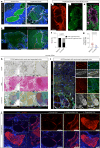
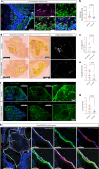
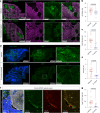
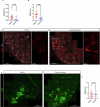
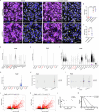
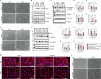
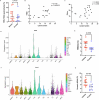
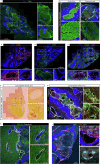
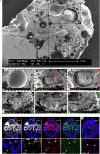
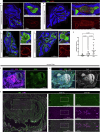
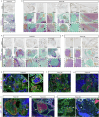
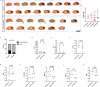
Cerebral cavernous malformation (CCM) is a neurovascular disease with symptoms such as strokes, hemorrhages and neurological deficits. With surgery being the only treatment strategy, understanding the molecular mechanisms of CCM is crucial in finding alternative therapeutic options for CCM. Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) were recently reported in CCM, and NETs were shown to have positive or negative effects in different disease contexts. In this study, we investigated the roles of NETs in CCM by pharmacologically inhibiting NET formation using Cl-amidine (a peptidyl arginine deiminase inhibitor). We show here that Cl-amidine treatment reduced lesion burden, coagulation and endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Furthermore, NETs promoted the activation of microglia and fibroblasts, leading to increased neuroinflammation and a chronic wound microenvironment in CCM. The inhibition of NET formation caused endothelial quiescence and promoted a healthier microenvironment. Our study suggests the inhibition of NETs as a potential therapeutic strategy in CCM.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
