Using isotopic lead and strontium in sediments to trace natural and anthropogenic sources in the Bohai Sea
- PMID: 39632994
- PMCID: PMC11618753
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-81493-w
Using isotopic lead and strontium in sediments to trace natural and anthropogenic sources in the Bohai Sea
Abstract
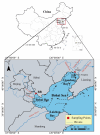
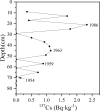
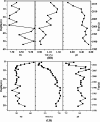
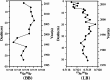
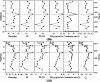
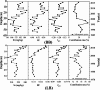
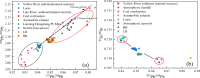
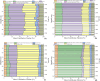
The containment history in the coastal zone of the Bohai Sea has not been sufficiently traced because of the difficulty in identifying complex sources of pollutants. This study quantitatively identified various sources of Pb and Sr in two tidal flat sediment cores from Bohai Bay (core BB) and Liaodong Bay (core LB) based on their isotope ratios to trace the natural and anthropogenic disturbance history in the Bohai Sea. The results showed that natural inputs of Pb were the main sources for cores BB and LB; however, core LB was more influenced by anthropogenic inputs. Natural inputs were derived mainly from Chinese loess and Yellow River sediments, whereas anthropogenic sources were mainly a mixture of vehicular exhaust emissions before 2000 and coal combustion after 2000. Anthropogenic influence has declined since the late 1990s, especially in Bohai Bay, but has increased in Liaodong Bay from 1998 to 2006.
Keywords: Historical variation; Pb isotope ratios; Sediment cores; Source identification; Sr isotope ratios.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Historical record of lead accumulation and source in the tidal flat of Haizhou Bay, Yellow Sea: Insights from lead isotopes.Mar Pollut Bull. 2016 May 15;106(1-2):383-7. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.02.046. Epub 2016 Mar 3. Mar Pollut Bull. 2016. PMID: 26947927
-
Isotopic identification of natural vs. anthropogenic lead sources in marine sediments from the inner Ría de Vigo (NW Spain).Sci Total Environ. 2012 Oct 15;437:22-35. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.07.063. Epub 2012 Aug 17. Sci Total Environ. 2012. PMID: 22903001
-
137Cs and 239+240Pu in the Bohai Sea of China: Comparison in distribution and source identification between the inner bay and the tidal flat.Mar Pollut Bull. 2019 Jan;138:604-617. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.12.005. Epub 2018 Dec 17. Mar Pollut Bull. 2019. PMID: 30660312
-
Distributions and sources of heavy metals in sediments of the Bohai Sea, China: a review.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017 Nov;24(32):24753-24764. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-0330-6. Epub 2017 Oct 5. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28983722 Review.
-
Pollution status of the Bohai Sea: an overview of the environmental quality assessment related trace metals.Environ Int. 2014 Jan;62:12-30. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2013.09.019. Epub 2013 Oct 23. Environ Int. 2014. PMID: 24161379 Review.
References
-
- Herbeck, L. S., Unger, D., Wu, Y. & Jennerjahn, T. C. Effluent, nutrient and organic matter export from shrimp and fish ponds causing eutrophication in coastal and back-reef waters of NE Hainan, tropical China. Cont. Shelf Res.57, 92–104 (2013).
-
- Chen, X. et al. Topological and dynamic complexity of the Pearl River Delta and its responses to human intervention. J. Hydrol.608, 127619. 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.127619 (2022).
-
- Xiang, L., Yang, J., Wang, Y., Liu, Q. & Zhang, G. Distribution, source, and contamination assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of the Old Yellow River Estuary in China. Mar. Pollut Bull.194, 115416. 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2023.115416 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Szefer, P., Glasby, G. P., Pempkowiak, J. & Kaliszan, R. Extraction studies of heavy-metal pollutants in surficial sediments from the southern Baltic Sea off Poland. Chem. Geol.120, 111–126. 10.1016/0009-2541(94)00103-F (1995).
-
- Chatterjee, M. et al. Distribution and possible source of trace elements in the sediment cores of a tropical macrotidal estuary and their ecotoxicological significance. Environ. Int.33, 346–356. 10.1016/j.envint.2006.11.013 (2007). - PubMed
Grants and funding
- ZHTD202106/Research for Resource Utilization and Environmental Remediation in the Coastal Zone
- ZHTD202106/Research for Resource Utilization and Environmental Remediation in the Coastal Zone
- ZHTD202106/Research for Resource Utilization and Environmental Remediation in the Coastal Zone
- ZHTD202106/Research for Resource Utilization and Environmental Remediation in the Coastal Zone
- ZHTD202106/Research for Resource Utilization and Environmental Remediation in the Coastal Zone
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

