Compound-Specific Isotope Analysis as a Potential Approach for Investigation of Cerebral Accumulation of Docosahexaenoic Acid: Previous Milestones and Recent Trends
- PMID: 39633088
- PMCID: PMC11953176
- DOI: 10.1007/s12035-024-04643-1
Compound-Specific Isotope Analysis as a Potential Approach for Investigation of Cerebral Accumulation of Docosahexaenoic Acid: Previous Milestones and Recent Trends
Abstract
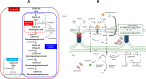
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA, C22:6 n-3), a predominant omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid in brain, plays a vital role in cerebral development and exhibits functions with potential therapeutic effects (synaptic function, neurogenesis, brain inflammation regulation) in neurodegenerative diseases. The most common approaches of studying the cerebral accretion and metabolism of DHA involve the use of stable or radiolabeled tracers. Although these methods approved kinetic modeling of ratios and turnovers for fatty acids, they are associated with excessive costs, restrictive studies, and singular dosing effects. Compound-specific isotope analysis (CSIA) is recognized as a cost-effective alternative approach for investigating DHA metabolism in vitro and in vivo. This method involves determining variations in 13C content to identify the sources of specific compounds. This review comprehensively discusses a summary of different methods and recent advancements in CSIA application in studying DHA turnover in brain. Following, the ability and applications of CSIA by using gas-chromatography combined with isotope ratio mass-spectrometry to differentiate between natural endogenous DHA in brain and exogenous DHA are also highlighted. In general, the efficiency of CSIA has been demonstrated in utilizing natural 13C enrichment to distinguish between the incorporation of newly synthesized or pre-existing DHA into the brain and other body tissues, eliminating the need of tracers. This review provides comprehensive knowledge, which will have potential applications in both academia and industry for advancing the understanding in neurobiology and enhancing the development of nutritional strategies and pharmaceutical interventions targeting brain health.
Keywords: Bioavailability, Neurological disorders; Brain; CSIA; Docosahexaenoic acid; GC-IRMS.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate: Not applicable. Consent for Publication: Not applicable. Competing Interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Arab-Tehrany E et al (2012) Beneficial effects and oxidative stability of omega-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids. Trends Food Sci Technol 25(1):24–33
-
- Yadav P, Chauhan AK, and Al-Sebaeai MA (2020) Omega-3 Fatty Acid from Plant Sources and Its Application in Food Technology. Innovations in Food Technology: Current Perspectives and Future Goals 41–52.
-
- Pandohee J (2022) Alpha-linolenic acid. Nutraceuticals and Health Care. Elsevier, pp 279–288
-
- Domenichiello AF, Kitson AP, Bazinet RP (2015) Is docosahexaenoic acid synthesis from α-linolenic acid sufficient to supply the adult brain? Prog Lipid Res 59:54–66 - PubMed
-
- Lacombe RS, Chouinard-Watkins R, Bazinet RP (2018) Brain docosahexaenoic acid uptake and metabolism. Mol Aspects Med 64:109–134 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

