A Novel Self-Supervised Learning-Based Method for Dynamic CT Brain Perfusion Imaging
- PMID: 39633209
- PMCID: PMC12343401
- DOI: 10.1007/s10278-024-01341-1
A Novel Self-Supervised Learning-Based Method for Dynamic CT Brain Perfusion Imaging
Abstract
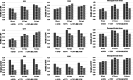
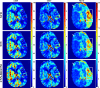
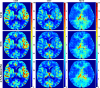
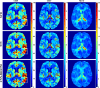
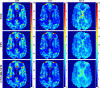
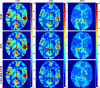
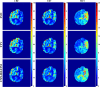
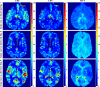
Dynamic computed tomography (CT)-based brain perfusion imaging is a non-invasive technique that can provide quantitative measurements of cerebral blood flow (CBF), cerebral blood volume (CBV), and mean transit time (MTT). However, due to high radiation dose, dynamic CT scan with a low tube voltage and current protocol is commonly used. Because of this reason, the increased noise degrades the quality and reliability of perfusion maps. In this study, we aim to propose and investigate the feasibility of utilizing a convolutional neural network and a bi-directional long short-term memory model with an attention mechanism to self-supervisedly yield the impulse residue function (IRF) from dynamic CT images. Then, the predicted IRF can be used to compute the perfusion parameters. We evaluated the performance of the proposed method using both simulated and real brain perfusion data and compared the results with those obtained from two existing methods: singular value decomposition and tensor total-variation. The simulation results showed that the overall performance of parameter estimation obtained from the proposed method was superior to that obtained from the other two methods. The experimental results showed that the perfusion maps calculated from the three studied methods were visually similar, but small and significant differences in perfusion parameters between the proposed method and the other two methods were found. We also observed that there were several low-CBF and low-CBV lesions (i.e., suspected infarct core) found by all comparing methods, but only the proposed method revealed longer MTT. The proposed method has the potential to self-supervisedly yield reliable perfusion maps from dynamic CT images.
Keywords: Bi-directional long short-term memory; Computed tomography perfusion; Convolutional neural network; Self-supervised learning.
© 2024. The Author(s) under exclusive licence to Society for Imaging Informatics in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics Approval: No institutional review board is required. Consent to Participate: Written informed consent was not required for this study because this is a retrospective study. Consent for Publication: Not applicable. Competing Interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Regional cerebral blood flow single photon emission computed tomography for detection of Frontotemporal dementia in people with suspected dementia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jun 23;2015(6):CD010896. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010896.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26102272 Free PMC article.
-
Unsupervised learning based perfusion maps for temporally truncated CT perfusion imaging.Phys Med Biol. 2025 Aug 14;70(16). doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/adf7fd. Phys Med Biol. 2025. PMID: 40763789
-
Magnetic resonance perfusion for differentiating low-grade from high-grade gliomas at first presentation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 22;1(1):CD011551. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011551.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29357120 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Validation of a Convolutional Neural Network Model to Predict a Pathologic Fracture in the Proximal Femur Using Abdomen and Pelvis CT Images of Patients With Advanced Cancer.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2023 Nov 1;481(11):2247-2256. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000002771. Epub 2023 Aug 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2023. PMID: 37615504 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
