Blood pressure management protocol based on transtheoretical model effectiveness on self- care: A systematic review
- PMID: 39633620
- PMCID: PMC11612347
- DOI: 10.34172/hpp.42814
Blood pressure management protocol based on transtheoretical model effectiveness on self- care: A systematic review
Abstract
Background: Hypertension is a prevalent medical condition associated with cardiovascular and kidney diseases, leading to premature death and disability. Despite medication use, hypertension continues to rise due to unhealthy lifestyles. Self-care strategies play crucial roles in effectively treating hypertension. We aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions based on the transtheoretical model (TTM) in improving self-care, self-efficacy, and health-related quality of life (HRQOL) in hypertensive adults.
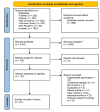
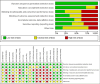
Methods: A comprehensive search was performed in multiple databases using appropriate search strategies. Two independent reviewers screened articles, and assessed their adherence to the inclusion and exclusion criteria. The risk of bias in randomized controlled trials was assessed by the Cochrane Collaboration tool and quasi-experimental studies using the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) Critical Appraisal Checklist for Quasi-Experimental Studies.
Results: The review included 24 studies with a total of 6553 participants. Most interventions aimed to encourage a healthier lifestyle and improve diet and physical activity. The message was delivered through various methods such as slide/tape messages, individual education/counseling sessions, telephone-delivered interventions, and multimedia training software based on the TTM. Control groups received physician visits or attended lifestyle lectures but did not receive specific behavior change programs like the intervention groups.
Conclusion: Our results indicated that the TTM and stage of change model can be an appropriate framework for delivering educational messages to patients.
Keywords: Hypertension; Self-care; Self-management; Systematic review; Transtheoretical model.
©2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no competing interests.
Similar articles
-
Promoting and supporting self-management for adults living in the community with physical chronic illness: A systematic review of the effectiveness and meaningfulness of the patient-practitioner encounter.JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2009;7(13):492-582. doi: 10.11124/01938924-200907130-00001. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2009. PMID: 27819974
-
Effectiveness of interventions that assist caregivers to support people with dementia living in the community: a systematic review.Int J Evid Based Healthc. 2008 Jun;6(2):137-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-1609.2008.00090.x. Int J Evid Based Healthc. 2008. PMID: 21631819
-
Effectiveness of avatar-based technology in patient education for improving chronic disease knowledge and self-care behavior: a systematic review.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2019 Jun;17(6):1101-1129. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2017-003905. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2019. PMID: 31021975
-
Behavioural interventions for type 2 diabetes: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2009;9(21):1-45. Epub 2009 Oct 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2009. PMID: 23074526 Free PMC article.
-
Transtheoretical model-based nutritional interventions in adolescents: a systematic review.BMC Public Health. 2020 Oct 14;20(1):1543. doi: 10.1186/s12889-020-09643-z. BMC Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33054748 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS. ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association. Task force on clinical practice guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;7(1):68–74. doi: 10.22141/2307-1257.7.1.2018.122220. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Forouzanfar MH, Alexander L, Anderson HR, Bachman VF, Biryukov S, Brauer M, et al. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 79 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks in 188 countries, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2015;386(10010):2287–323. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(15)00128-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources