Noncoding RNA, friend or foe for nephrolithiasis?
- PMID: 39633711
- PMCID: PMC11614778
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1457319
Noncoding RNA, friend or foe for nephrolithiasis?
Abstract
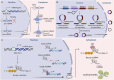
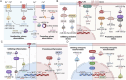
Nephrolithiasis is one of the most common diseases in urology, characterized by notable incidence and recurrence rates, leading to significant morbidity and financial burden. Despite its prevalence, the precise mechanisms underlying stone formation remain incompletely understood, thus hindering significant advancements in kidney stone management over the past three decades. Investigating the pivotal biological molecules that govern stone formation has consistently been a challenging and high-priority task. A significant portion of mammalian genomes are transcribed into noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs), which have the ability to modulate gene expression and disease progression. They are thus emerging as a novel target class for diagnostics and pharmaceutical exploration. In recent years, the role of ncRNAs in stone formation has attracted burgeoning attention. They have been found to influence stone formation by regulating ion transportation, oxidative stress injury, inflammation, osteoblastic transformation, autophagy, and pyroptosis. These findings contributes new perspectives on the pathogenesis of nephrolithiasis. To enhance our understanding of the diagnostic and therapeutic potential of nephrolithiasis-associated ncRNAs, we summarized the expression profiles, biological functions, and clinical significance of these ncRNAs in the current review.
Keywords: biomarkers; calcium oxalate; ncRNAs; nephrolithiasis; therapeutic targets.
Copyright © 2024 Wang, Yang, Chen, Yang and Jiang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Non-Coding RNAs in Kidney Stones.Biomolecules. 2024 Feb 11;14(2):213. doi: 10.3390/biom14020213. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38397450 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitexin exerts protective effects against calcium oxalate crystal-induced kidney pyroptosis in vivo and in vitro.Phytomedicine. 2021 Jun;86:153562. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153562. Epub 2021 Mar 29. Phytomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33857849
-
Autophagy-endoplasmic reticulum stress inhibition mechanism of superoxide dismutase in the formation of calcium oxalate kidney stones.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Jan;121:109649. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109649. Epub 2019 Nov 13. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 31733571
-
Understanding formation processes of calcareous nephrolithiasis in renal interstitium and tubule lumen.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Apr;28(7):e18235. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18235. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38509735 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PPARγ agonist alleviates calcium oxalate nephrolithiasis by regulating mitochondrial dynamics in renal tubular epithelial cell.PLoS One. 2024 Sep 26;19(9):e0310947. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0310947. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39325731 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

