LAMP5, One of Four Genes Related to Oxidative Stress That Predict Biochemical Recurrence-Free Survival, Promotes Proliferation and Invasion in Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 39634037
- PMCID: PMC11616484
- DOI: 10.2147/AABC.S489131
LAMP5, One of Four Genes Related to Oxidative Stress That Predict Biochemical Recurrence-Free Survival, Promotes Proliferation and Invasion in Prostate Cancer
Retraction in
-
LAMP5, One of Four Genes Related to Oxidative Stress That Predict Biochemical Recurrence-Free Survival, Promotes Proliferation and Invasion in Prostate Cancer [Retraction].Adv Appl Bioinform Chem. 2025 Mar 6;18:1-2. doi: 10.2147/AABC.S526200. eCollection 2025. Adv Appl Bioinform Chem. 2025. PMID: 40084236 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Prostate cancer (PCa) development largely depends on increased levels of oxidative stress (OS) and a deficient anti-oxidative system. Identifying genes associated with oxidative stress is critical in order to direct PCa therapy and future research.
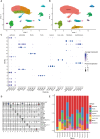
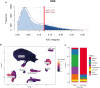
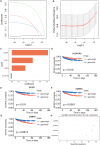
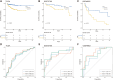
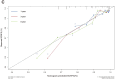
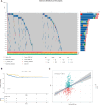
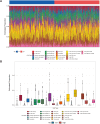
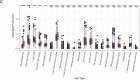
Methods: The TCGA and GTEx databases provided the bulk RNA-seq data, and the GEO database provided the single-cell data GSE141445. Utilizing reactive oxygen species (ROS) markers, single-cell analysis and cluster identification related to oxidative stress were conducted using the R packages "Seurat" and "AUCell". The differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in normal and PCa samples were identified with the "limma" R package. LASSO regression analysis was used to build a recurrence score (RS) model. The R packages "maftools" and the CIBERSORT method were employed to explore genetic mutation and the infiltrating immune cell, respectively. LAMP5 was chosen for further investigation after random forest analysis was performed.
Results: The RS model for PCa was found to be an independent predictor. The tumor immune microenvironment and the frequency of gene mutations differed significantly between the high- and low-risk score groups. Further investigation revealed that downregulation of LAMP5 in PC-3 and DU145 cell lines suppressed cell proliferation and invasion, as demonstrated by the results of in vitro experiments.
Conclusion: We successfully created a robust RS model. The result of the study indicates that LAMP5 could contribute to cell proliferation and invasion in PCa.
Keywords: LAMP5; oxidative stress; prostate cancer; recurrence score model; single-cell analysis.
© 2024 Wu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Roach M, Hanks G, Thames H, et al. Defining biochemical failure following radiotherapy with or without hormonal therapy in men with clinically localized prostate cancer: recommendations of the RTOG-ASTRO phoenix consensus conference. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006;65(4):965–974. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.04.029 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

