Epitope-imprinted biomaterials with tailor-made molecular targeting for biomedical applications
- PMID: 39634057
- PMCID: PMC11616479
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.11.012
Epitope-imprinted biomaterials with tailor-made molecular targeting for biomedical applications
Abstract
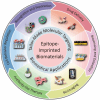
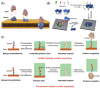
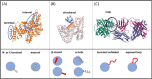
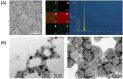
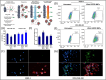
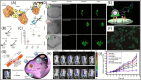
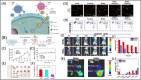
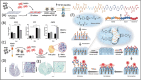
Molecular imprinting technology (MIT), a synthetic strategy to create tailor-made molecular specificity, has recently achieved significant advancements. Epitope imprinting strategy, an improved MIT by imprinting the epitopes of biomolecules (e.g., proteins and nucleic acids), enables to target the entire molecule through recognizing partial epitopes exposed on it, greatly expanding the applicability and simplifying synthesis process of molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs). Thus, epitope imprinting strategy offers promising solutions for the fabrication of smart biomaterials with molecular targeting and exhibits wide applications in various biomedical scenarios. This review explores the latest advances in epitope imprinting techniques, emphasizing selection of epitopes and functional monomers. We highlight the significant improvements in specificity, sensitivity, and stability of these materials, which have facilitated their use in bioanalysis, clinical therapy, and pharmaceutical development. Additionally, we discuss the application of epitope-imprinted materials in the recognition and detection of peptides, proteins, and cells. Despite these advancements, challenges such as template complexity, imprinting efficiency, and scalability remain. This review addresses these issues and proposes potential directions for future research to overcome these barriers, thereby enhancing the efficacy and practicality of epitope molecularly imprinting technology in biomedical fields.
Keywords: Cell recognition; Drug delivery; Epitope imprinting; Molecular targeting; Synthetic antibody.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that no conflict of interest in this paper.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

