Free-space-coupled wavelength-scale disk resonators
- PMID: 39634088
- PMCID: PMC11501722
- DOI: 10.1515/nanoph-2022-0106
Free-space-coupled wavelength-scale disk resonators
Abstract
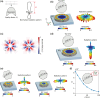
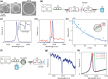
Optical microresonators with low quality factor ( ) can be efficiently excited by and scatter freely propagating optical waves, but those with high typically cannot. Here, we present a universal model for resonators interacting with freely propagating waves and show that the stored energy of a resonator excited by a plane wave is proportional to the product of its and directivity. Guided by this result, we devise a microdisk with periodic protrusions in its circumference that couples efficiently to normally incident plane waves. We experimentally demonstrate several microdisk designs, including one with a radius of 0.75 and of 15,000. Our observation of thermally-induced bistability in this resonator at input powers as low as 0.7 mW confirms strong excitation. Their small footprints and mode volumes and the simplicity of their excitation and fabrication make wavelength-scale, free-space-coupled microdisks attractive for sensing, enhancing emission and nonlinearity, and as micro-laser cavities.
Keywords: flat optics; free space coupling; microresonators.
© 2022 Babak Mirzapourbeinekalaye et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston.
Figures

References
-
- Yao Z., Wu K., Tan B. X., et al. Integrated silicon photonic microresonators: emerging technologies. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant. Electron. . 2018;24:1–24. doi: 10.1109/jstqe.2018.2846047. - DOI
-
- Ellis B., Mayer M. A., Shambat G., et al. Ultralow-threshold electrically pumped quantum-dot photonic-crystal nanocavity laser. Nat. Photonics . 2011;5:297–300. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2011.51. - DOI
-
- Decker M., Staude I., Falkner M., et al. High-efficiency dielectric Huygens’ surfaces. Adv. Opt. Mater. . 2015;3:813–820. doi: 10.1002/adom.201400584. - DOI
-
- Yu Y. F., Zhu A. Y., Paniagua-Dominguez R., et al. High-transmission dielectric metasurface with 2pi phase control at visible wavelengths. Laser Photon. Rev. . 2015;9:412–418. doi: 10.1002/lpor.201500041. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
