Histatins, proangiogenic molecules with therapeutic implications in regenerative medicine
- PMID: 39634559
- PMCID: PMC11615599
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.111309
Histatins, proangiogenic molecules with therapeutic implications in regenerative medicine
Abstract
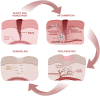
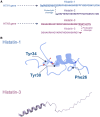
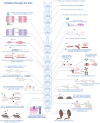
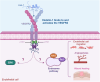
Recent studies show that a group of salivary peptides, collectively known as histatins, are potent inducers of wound healing in both soft and hard tissues. Among these molecules, histatin-1 stands out for its ability to stimulate the repair of skin, oral mucosal, and osseous tissue. Remarkably, all these effects are associated with the capacity of histatin-1 to promote angiogenesis via inducing endothelial cell adhesion, migration, and signaling. These findings have opened new opportunities in the field of regenerative medicine, leading to an increasing number of articles and patents proposing therapeutic uses of histatin-1. However, this scenario raises a relevant concern regarding the appropriate use of these molecules, since, unlike the mode of action, little is known about the molecular mechanism by which they promote angiogenesis and wound healing. Recent studies shed light on the pharmacodynamics of histatin-1, by identifying the endothelial receptor that it binds and downstream signaling. This perspective will discuss current evidence on the role of histatins in wound healing and angiogenesis, emphasizing their impact on regenerative medicine.
Keywords: Biological sciences; Health sciences; Medicine; Natural sciences; Physiology.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
References
-
- Mateluna C., Torres P., Rodriguez-Peña M., Silva P., Matthies D.J., Criollo A., Bikker F.J., Bolscher J.G.M., Wilson C.A.M., Zapata-Torres G., Torres V.A. Identification of VEGFR2 as the Histatin-1 receptor in endothelial cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022;201 doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2022.115079. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

