Combatting biofilm-mediated infections in clinical settings by targeting quorum sensing
- PMID: 39634722
- PMCID: PMC11615143
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tcsw.2024.100133
Combatting biofilm-mediated infections in clinical settings by targeting quorum sensing
Abstract
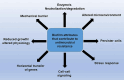
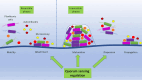
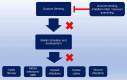
Biofilm-associated infections constitute a significant challenge in managing infectious diseases due to their high resistance to antibiotics and host immune responses. Biofilms are responsible for various infections, including urinary tract infections, cystic fibrosis, dental plaque, bone infections, and chronic wounds. Quorum sensing (QS) is a process of cell-to-cell communication that bacteria use to coordinate gene expression in response to cell density, which is crucial for biofilm formation and maintenance.. Its disruption has been proposed as a potential strategy to prevent or treat biofilm-associated infections leading to improved treatment outcomes for infectious diseases. This review article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the literature on QS-mediated disruption of biofilms for treating infectious diseases. It will discuss the mechanisms of QS disruption and the various approaches that have been developed to disrupt QS in reference to multiple clinical pathogens. In particular, numerous studies have demonstrated the efficacy of QS disruption in reducing biofilm formation in various pathogens, including Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Finally, the review will discuss the challenges and future directions for developing QS disruption as a clinical therapy for biofilm-associated infections. This includes the development of effective delivery systems and the identification of suitable targets for QS disruption. Overall, the literature suggests that QS disruption is a promising alternative to traditional antibiotic treatment for biofilm-associated infections and warrants further investigation.
Keywords: AMR; Antibiofilm strategy; Antibiotic resistance; Biofilms; Infectious diseases; QSI (Quorum sensing inhibition).
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources