Scaling up multispectral color filters with binary lithography and reflow (BLR)
- PMID: 39635033
- PMCID: PMC11465983
- DOI: 10.1515/nanoph-2024-0090
Scaling up multispectral color filters with binary lithography and reflow (BLR)
Abstract
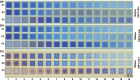
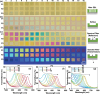
Efforts to increase the number of filters are driven by the demand for miniaturized spectrometers and multispectral imaging. However, processes that rely on sequential fabrication of each filter are cost ineffective. Herein, we introduce an approach to produce at least 16 distinct filters based on a single low-resolution lithographic step with minimum feature size of 0.6 μm. Distinct from grayscale lithography, we employ standard binary lithography but achieve height variations in polymeric resist through a post-development reflow process. The resulting transparent polymeric films were incorporated in Fabry-Perot cavity structures with cavity thickness ranging from 90 to 230 nm to produce transmittance across the visible spectrum. This binary lithography and reflow (BLR) process demonstrates control of the dielectric layer thickness down to ∼15 nm. This new process provides a cost-effective alternative to traditional techniques in fabricating microscopic transmission filters, and other applications where precise thickness variation across the substrate is required.
Keywords: binary lithography and reflow; electron beam lithography; multispectral filters; structural colors.
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Wang P., Menon R., Thomas J., Gouton P. Ultra-high-sensitivity color imaging via a transparent diffractive-filter array and computational optics. Optica . 2015;2(11):933–939. doi: 10.1364/optica.2.000933. - DOI
-
- Kristensen A., et al. Plasmonic colour generation. Nat. Rev. Mater. . 2016;2(1):16088(1)–16088(14). doi: 10.1038/natrevmats.2016.88. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
