Multi-faceted plasmonic nanocavities
- PMID: 39635199
- PMCID: PMC11501932
- DOI: 10.1515/nanoph-2023-0392
Multi-faceted plasmonic nanocavities
Abstract
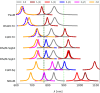
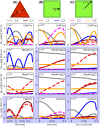
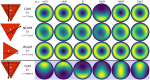
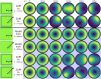
Plasmonic nanocavities form very robust sub-nanometer gaps between nanometallic structures and confine light within deep subwavelength volumes to enable unprecedented control of light-matter interactions. However, spherical nanoparticles acquire various polyhedral shapes during their synthesis, which has a significant impact in controlling many light-matter interactions, such as photocatalytic reactions. Here, we focus on nanoparticle-on-mirror nanocavities built from three polyhedral nanoparticles (cuboctahedron, rhombicuboctahedron, decahedron) that commonly occur during the synthesis. Their photonic modes have a very intricate and rich optical behaviour, both in the near- and far-field. Through a recombination technique, we obtain the total far-field produced by a molecule placed within these nanocavities, to reveal how energy couples in and out of the system. This work paves the way towards understanding and controlling light-matter interactions, such as photocatalytic reactions and non-linear vibrational pumping, in such extreme environments.
Keywords: crystallization facet; facet; nanocavity; nanogap; nanoparticle; quasi-normal modes.
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Thacker V. V., Herrmann L. O., Sigle D. O., et al. DNA origami based assembly of gold nanoparticle dimers for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Nat. Commun. . 2014;5 3448. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
