Salvage of cardiopulmonary collapse caused by ethanol sclerotherapy for vascular malformations: clinical experience at a single center and literature review
- PMID: 39635268
- PMCID: PMC11614990
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1439839
Salvage of cardiopulmonary collapse caused by ethanol sclerotherapy for vascular malformations: clinical experience at a single center and literature review
Abstract
Objective: This review aims to summarize the salvage experience of cardiopulmonary collapse occurring as a result of absolute ethanol sclerotherapy for vascular malformations.
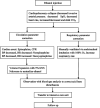
Methods: In total, we reviewed three cases of cardiopulmonary collapse induced by ethanol sclerotherapy for vascular malformations and described the details of the salvage procedure. Saturation of pulse oxygen (SpO2), end-tidal CO2, and invasive arterial pressure were the routine monitors for ethanol injection patients. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation, epinephrine, norepinephrine, and deoxyepinephrine were mainly used to correct circulation parameters. Manually ventilated via endotracheal intubation with 100% O2, increased respiratory rate were mainly used to correct Respiratory parameters.
Results: All three cases were successfully salvaged without major complications. When cardiopulmonary collapse occurred, manual ventilation via endotracheal intubation with 100% O2, increased ventilation frequency and external cardiac compression were the emergency treatments. Epinephrine, norepinephrine, deoxyepinephrine infusion solely or combined were crucial to maintaining the basic vital signs.
Conclusion: Despite the severity of cardiopulmonary collapse caused by ethanol sclerotherapy, it can be detected by close observation and reversed with timely treatment.
Keywords: cardiopulmonary collapse; emergency; ethanol; sclerotherapy; vascular malformations.
© 2024 Su, Zhao, Shen, Fan, Wang, Wang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The reviewer XL declared a shared affiliation with the author(s) to the handling editor at the time of review.
Figures
Similar articles
-
2005 American Heart Association (AHA) guidelines for cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and emergency cardiovascular care (ECC) of pediatric and neonatal patients: pediatric basic life support.Pediatrics. 2006 May;117(5):e989-1004. doi: 10.1542/peds.2006-0219. Pediatrics. 2006. PMID: 16651298
-
Sclerotherapy after embolization of draining vein: a safe treatment method for venous malformations.J Vasc Surg. 2008 Jun;47(6):1292-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2008.01.010. Epub 2008 Apr 3. J Vasc Surg. 2008. PMID: 18387776
-
Cardiovascular collapse due to right heart failure following ethanol sclerotherapy: a case report.Korean J Anesthesiol. 2014 May;66(5):388-91. doi: 10.4097/kjae.2014.66.5.388. Epub 2014 May 26. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2014. PMID: 24910732 Free PMC article.
-
Outcomes and complications of sclerotherapy for venous malformations.Vasc Endovascular Surg. 2013 Aug;47(6):454-61. doi: 10.1177/1538574413492390. Epub 2013 Jun 11. Vasc Endovascular Surg. 2013. PMID: 23759722 Review.
-
Sclerotherapy for cervical cystic lymphatic malformations in children. Our experience with computed tomography-guided 98% sterile ethanol insertion and a review of the literature.J Pediatr Surg. 2010 Dec;45(12):2473-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2010.07.023. J Pediatr Surg. 2010. PMID: 21129570 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources