The predictive values of C-reactive protein-neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio for the risk of refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 39635861
- PMCID: PMC11648507
- DOI: 10.1017/S0950268824001134
The predictive values of C-reactive protein-neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio for the risk of refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children: a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
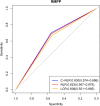
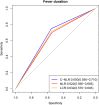
This cohort study evaluated the associations of C-reactive protein-neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (C-NLR) and lymphocyte-CRP ratio (LCR) with refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia (RMPP), and the predictive values of C-NLR and LCR for RMPP and prolonged fever in children based on 389 children with MPP. The associations of NLR, C-NLR, and LCR with RMPP and prolonged fever were evaluated by logistic regression analysis. C-NLR was correlated with an increased risk of RMPP in children [odds ratio (OR) = 3.459, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.598-7.491]. A higher risk of RMPP was identified in the C-NLR > 29.9 group (OR = 2.885, 95% CI: 1.599-5.203). LCR > 1584.2 was associated with a decreased risk of RMPP (OR = 0.500, 95% CI: 0.282-0.887). Increased risk of prolonged fever in children was identified with the increase of C-NLR (OR = 5.913, 95% CI: 2.335-14.972) or NLR (OR = 2.413, 95% CI: 1.689-3.446). The AUCs of C-NLR, LCR, and NLR for predicting RMPP were 0.630, 0.623, and 0.608, respectively. In conclusion, C-NLR was associated with increased RMPP risk in children and had good value for predicting RMPP and prolonged fever in children.
Keywords: C-reactive protein-neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio; lymphocyte-CRP ratio; neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio; refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a predictor of poor outcomes of Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia.Front Immunol. 2023 Dec 19;14:1302702. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1302702. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38169689 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical significance of D-dimer levels in refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia.BMC Infect Dis. 2021 Jan 6;21(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-05700-5. BMC Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33407216 Free PMC article.
-
Recognition of refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia among Myocoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in hospitalized children: development and validation of a predictive nomogram model.BMC Pulm Med. 2023 Oct 10;23(1):383. doi: 10.1186/s12890-023-02684-1. BMC Pulm Med. 2023. PMID: 37817172 Free PMC article.
-
Refractory Mycoplasma Pneumonia in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Laboratory Features and Predictors.J Immunol Res. 2022 Jun 26;2022:9227838. doi: 10.1155/2022/9227838. eCollection 2022. J Immunol Res. 2022. PMID: 35795531 Free PMC article.
-
The risk factors of children acquiring refractory mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Mar 19;100(11):e24894. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000024894. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 33725960 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Che-Morales JL and Cortes-Telles A (2019) Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a serum biomarker associated with community acquired pneumonia. Revista Médica del Instituto Mexicano del Seguro Social 56(6), 537–543. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous