Acute pilonidal abscess: Prospective nationwide audit in the Netherlands
- PMID: 39635960
- PMCID: PMC11683315
- DOI: 10.1111/codi.17254
Acute pilonidal abscess: Prospective nationwide audit in the Netherlands
Abstract
Aim: The aim of this study was to assess Dutch surgical practice and outcomes for acute pilonidal abscess.
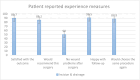
Method: Patients with pilonidal sinus disease (PSD) who underwent surgical treatment between 1 March 2020 and 1 March 2021 at 36 participating hospitals were included in a prospective observational cohort study. For the present study, only patients with an acute abscess were included for analysis. Outcomes included symptoms, wound healing, time to resume daily activities and complications. Follow-up was 1 year and included questionnaires on recurrent abscesses, symptomatic chronic PSD, quality of life and patient-reported experience measures.
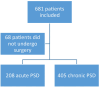
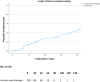
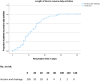
Results: Of 681 included patients, 208 presented with an acute pilonidal abscess. Incision and drainage (I&D) was performed in 205 of these patients (99%). The wound healing rate after I&D was 42.2% at the outpatient clinic, with a median time to closure of 43 days. The complication rate was 4.4%. One-year questionnaires were completed by 158 out of 205 patients (77.1%). Fifteen patients (7.3%) had a recurrent abscess within 1 year. The symptomatic chronic PSD rate was 8.8%.
Conclusion: Of all the patients presenting with PSD in this prospective national study cohort, 30% had a pilonidal abscess. Incision and drainage showed a low complication rate but successful wound healing in less than half of the patients. The study showed that 91.2% of patients did not undergo additional surgical treatment for symptomatic chronic PSD within 1 year of follow-up.
Keywords: acute pilonidal abscesses; complications; incision and drainage; pilonidal sinus disease; recurrent abscesses; wound healing.
© 2024 The Author(s). Colorectal Disease published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Association of Coloproctology of Great Britain and Ireland.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Akinci OF , Bozer M, Uzunköy A, Düzgün SA, Coşkun A. Incidence and aetiological factors in pilonidal sinus among Turkish soldiers. Eur J Surg. 1999;165(4):339–342. - PubMed
-
- Brashear RI. Observations on the etiology of pilonidal diseases. South Med J. 1963;56:727–729. - PubMed
-
- Hueston JT. The aetiology of pilonidal sinuses. Br J Surg. 1953;41(167):307–311. - PubMed
-
- Hull TL, Wu J. Pilonidal disease. Surg Clin North Am. 2002;82(6):1169–1185. - PubMed
-
- Bissett IP, Isbister WH. The management of patients with pilonidal disease a comparative study. Aust NZ J Surg. 1987;57(12):939–942. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

