Gut microbiota CLA and IL-35 induction in macrophages through Gαq/11-mediated STAT1/4 pathway: an animal-based study
- PMID: 39636005
- PMCID: PMC11622586
- DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2024.2437253
Gut microbiota CLA and IL-35 induction in macrophages through Gαq/11-mediated STAT1/4 pathway: an animal-based study
Abstract
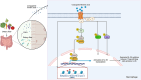
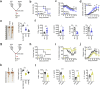
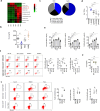
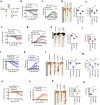
Gut microbiota/metabolites not only participate in the food and energy metabolism but also contribute to the host immune response and homeostasis. The alternation of gut microbiota/metabolites has been widely related to intestinal and extra-intestinal disorders such as intestinal bowel diseases (IBDs). Bactericidal substances from gut epithelial cells can regulate the composition of gut microbiota. However, the effects of regenerating protein 4 (REG4) (human)/(Reg4) (mice), a potentially bactericidal substance from gut epithelial cells, on the gut immune homeostasis maintain elusive. Here, we found that REG4/Reg4 is essential in maintaining gut immune homeostasis through REG4/Reg4 associated gut microbiota. Reg4 knockout (KO) mice were highly sensitive to DSS-mediated colitis, whereas human REG4 intestine epithelial cell transgenic (huREG4IECtg) mice exhibited more resistance to DSS-mediated colitis. Mechanistically, sequencing of gut microbiota and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry showed that REG4/Reg4 could affect the composition of gut microbiota. REG4/Reg4 associated gut microbiota such as Lactobacillus could metabolize linoleic acid (LA) into conjugated linoleic acid (CLA). Immunoprecipitation and immunoblot showed that CLA could effectively promote the expression of IL-35 in macrophages through Gαq/11 mediated activation STAT1/4. Thus, our results demonstrate that REG4/Reg4 plays a critical role in maintaining gut immune homeostasis through CLA-mediated IL-35+ macrophages.
Keywords: Conjugated linoleic acid; IL-35; Reg4; gut microbiota; macrophages.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Orally Administered CLA Ameliorates DSS-Induced Colitis in Mice via Intestinal Barrier Improvement, Oxidative Stress Reduction, and Inflammatory Cytokine and Gut Microbiota Modulation.J Agric Food Chem. 2019 Dec 4;67(48):13282-13298. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b05744. Epub 2019 Nov 15. J Agric Food Chem. 2019. PMID: 31690068
-
Gut microbiota-derived metabolite 3-idoleacetic acid together with LPS induces IL-35+ B cell generation.Microbiome. 2022 Jan 24;10(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s40168-021-01205-8. Microbiome. 2022. PMID: 35074011 Free PMC article.
-
Deficiency in intestinal epithelial Reg4 ameliorates intestinal inflammation and alters the colonic bacterial composition.Mucosal Immunol. 2019 Jul;12(4):919-929. doi: 10.1038/s41385-019-0161-5. Epub 2019 Apr 5. Mucosal Immunol. 2019. Retraction in: Mucosal Immunol. 2021 Mar;14(2):537. doi: 10.1038/s41385-020-00367-2. PMID: 30953001 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Gut microbiota derived indole-3-acetic acid ameliorates precancerous inflammatory intestinal milieu to inhibit tumorigenesis through IL-35.J Immunother Cancer. 2025 Apr 23;13(4):e011155. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2024-011155. J Immunother Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40274281 Free PMC article.
-
Cohousing-mediated microbiota transfer from milk bioactive components-dosed mice ameliorate colitis by remodeling colonic mucus barrier and lamina propria macrophages.Gut Microbes. 2021 Jan-Dec;13(1):1-23. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2021.1903826. Gut Microbes. 2021. PMID: 33789528 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A synbiotic combination of mixed probiotics and oligofructose restores intestinal microbiota disturbance in DSS-induced colitis in mice.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jul 24;16:1582155. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1582155. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40778208 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in gut-lung axis research: clinical perspectives on pneumonia prevention and treatment.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 22;16:1576141. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1576141. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40330490 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
