Gut microbiota regulates oxidative stress and inflammation: a double-edged sword in renal fibrosis
- PMID: 39636415
- PMCID: PMC11621299
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-024-05532-5
Gut microbiota regulates oxidative stress and inflammation: a double-edged sword in renal fibrosis
Abstract
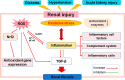
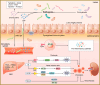
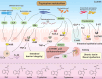
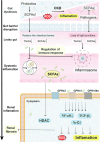
Gut microbiota is a complex and dynamic system that plays critical roles in human health and various disease. Progressive chronic kidney disease (CKD) suggests that patients irreversibly progress to end-stage kidney disease and need renal replacement treatments, including dialysis and transplantation. Ample evidence indicates that local oxidative stress and inflammation play pivotal roles in the pathogenesis and progression of CKD and dysbiosis of gut microbiota. CKD is always accompanied by intestinal inflammation and oxidative stress, which lead to rapid systemic translocation of bacterial-derived uraemic toxins, including indoxyl sulphate, phenyl sulphate and indole-3-acetic acid, and the consequent development and aggravation of renal fibrosis. Although inflammation and oxidative stress have been extensively discussed, there is a paucity of reports on the effects of gut microbiota on renal fibrosis and gut microbiota mediation of oxidative stress and inflammation. This review provides an overview of gut microbiota on inflammation and oxidative stress in renal fibrosis, briefly discusses regulation of the gut flora using microecological preparations and natural products, such as resveratrol, curcumin and emodin as treatments for CKD, and provides a clear pathophysiological rationale for the design of promising therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: Chronic kidney disease; Gut-kidney axis; Inflammation; Microecological preparations; Natural products; Oxidative stress.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interests: The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose. The authors report no declarations of interest. Ethical approval: Not applicable. Consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent to publish: Not applicable.
Figures
References
-
- Rashid I, Katravath P, Tiwari P, D’Cruz S, Jaswal S, Sahu G (2022) Hyperuricemia—a serious complication among patients with chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Explor Med 3:249–259 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

