Trial eligibility, treatment patterns, and outcome for venetoclax-based therapy in AML: a prospective cohort study
- PMID: 39637307
- PMCID: PMC11986219
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2024014014
Trial eligibility, treatment patterns, and outcome for venetoclax-based therapy in AML: a prospective cohort study
Abstract
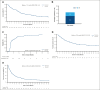
Venetoclax plus hypomethylating agents are considered standard of care for patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) judged ineligible for intensive chemotherapy (IC). Real-world studies complement clinical trials, because patterns of patient selection, treatment exposure, and postremission management may vary. This prospective observational multicenter study included 209 newly diagnosed IC-ineligible patients with a median age 75 years (interquartile range, 71-81 years). A high proportion of patients had secondary AML (53.7%), adverse-risk disease (35.3%), and complex karyotype (15.5%). At a median follow-up of 22.5 months (range, 0.1-43), median overall survival (mOS) was 11.7 months (95% confidence interval [CI], 9.9,15.4). Composite complete remission was achieved in 65.2% (CR, 44.4%; CR with incomplete hematologic recovery, 20.8%). Of responding patients, 21.1% underwent stem cell transplantation. When stratified based on VIALE-A original eligibility criteria, mOS was 17.8 months for patients meeting eligibility criteria and 10.7 months for patients who did not (P = .027). AML ontogeny (P = .024), reduced kidney function (P = .001), Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI; P = .0017), European LeukemiaNET (ELN) risk (P = .01), and body mass index (P = .0298) were significantly associated with OS. Multivariant Cox regression analysis confirmed independent association of OS with AML ontogeny (P = .012), CCI (P = .033), and ELN risk (P = .019). Patients enrolled in the latter half of the study period demonstrated improved OS than those enrolled earlier (P = .026). This prospective observational study highlights outcomes of patient subgroups, including those excluded from registration trials. This trial was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT03987958.
© 2025 American Society of Hematology. Published by Elsevier Inc. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: O.W. reports research support from AbbVie; speaker honoraria from AbbVie, Astellas, and Novartis; and an advisory role with AbbVie, Astellas, Novartis, Pfizer, Medison, and Teva. Y.M. reports an advisory role with AbbVie, Astellas, Bristol Myers Squibb, Gilead, Medison, Neopharm, Novartis, and Pfizer; and honoraria from and consultancy with AbbVie, Astellas, Medison, Novartis, and Takeda. B.N. reports speaker honoraria from and consultancy with AbbVie. Y.O., S.T., and G.S. report consultancy with AbbVie. T.T. reports research support from AbbVie. J.C. reports speaker honoraria from and consultancy with AbbVie. M.G., A.J.B., N.F., J.B., A.B., M.B., and R.C. report employment with AbbVie, and may hold stock or other options. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
A complete list of the members of the Israeli Acute Leukemia Working Group appears in “Appendix.”
Figures





References
-
- Döhner H, Wei AH, Appelbaum FR, et al. Diagnosis and management of AML in adults: 2022 recommendations from an international expert panel on behalf of the ELN. Blood. 2022;140(12):1345–1377. - PubMed
-
- DiNardo CD, Jonas BA, Pullarkat V, et al. Azacitidine and venetoclax in previously untreated acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(7):617–629. - PubMed
-
- Pratz KW, Jonas BA, Pullarkat V, et al. Long-term follow-up of VIALE-A: venetoclax and azacitidine in chemotherapy-ineligible untreated acute myeloid leukemia. Am J Hematol. 2024;99(4):615–624. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

