X-linked deletion of Crossfirre, Firre, and Dxz4 in vivo uncovers diverse phenotypes and combinatorial effects on autosomes
- PMID: 39638999
- PMCID: PMC11621363
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-54673-5
X-linked deletion of Crossfirre, Firre, and Dxz4 in vivo uncovers diverse phenotypes and combinatorial effects on autosomes
Abstract
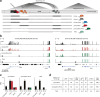
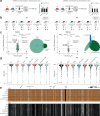
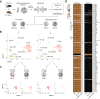
The lncRNA Crossfirre was identified as an imprinted X-linked gene, and is transcribed antisense to the trans-acting lncRNA Firre. The Firre locus forms an inactive-X-specific interaction with Dxz4, both loci providing the platform for the largest conserved chromatin structures. Here, we characterize the epigenetic profile of these loci, revealing them as the most female-specific accessible regions genome-wide. To address their in vivo role, we perform one of the largest X-linked knockout studies by deleting Crossfirre, Firre, and Dxz4 individually and in combination. Despite their distinct epigenetic features observed on the X chromosome, our allele-specific analysis uncovers these loci as dispensable for imprinted and random X chromosome inactivation. However, we provide evidence that Crossfirre affects autosomal gene regulation but only in combination with Firre. To shed light on the functional role of these sex-specific loci, we perform an extensive standardized phenotyping pipeline and uncover diverse knockout and sex-specific phenotypes. Collectively, our study provides the foundation for exploring the intricate interplay of conserved X-linked loci in vivo.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Kay, G. F., Barton, S. C., Surani, M. A. & Rastan, S. Imprinting and X chromosome counting mechanisms determine Xist expression in early mouse development. Cell77, 639–650 (1994). - PubMed
-
- Okamoto, I., Otte, A. P., Allis, C. D., Reinberg, D. & Heard, E. Epigenetic dynamics of imprinted X inactivation during early mouse development. Science303, 644–649 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Takagi, N. & Sasaki, M. Preferential inactivation of the paternally derived X chromosome in the extraembryonic membranes of the mouse. Nature256, 640–642 (1975). - PubMed
-
- Mak, W. et al. Reactivation of the paternal X chromosome in early mouse embryos. Science303, 666–669 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Barr, M. L. & Bertram, E. G. A morphological distinction between neurones of the male and female, and the behaviour of the nucleolar satellite during accelerated nucleoprotein synthesis. Nature163, 676 (1949). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

