Fine-tuning levels of filamins a and b as a specific mechanism sustaining Th2 lymphocyte functions
- PMID: 39639023
- PMCID: PMC11621393
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-53768-3
Fine-tuning levels of filamins a and b as a specific mechanism sustaining Th2 lymphocyte functions
Abstract
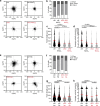
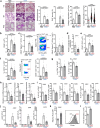
Augmenting the portfolio of therapeutics for type 2-driven diseases is crucial to address unmet clinical needs and to design personalized treatment schemes. An attractive therapy for such diseases would consist in targeting the recruitment of T helper 2 (Th2) lymphocytes to inflammatory sites. Herein, we show the degradation of filamins (FLN) a and b by the ASB2α E3 ubiquitin ligase as a mechanism sustaining Th2 lymphocyte functions. Low levels of FLNa and FLNb confer an elongated shape to Th2 lymphocytes associated with efficient αVβ3 integrin-dependent cell migration. Genes encoding the αVβ3 integrin and ASB2α belong to the core of Th2-specific genes. Using genetically modified mice, we find that increasing the levels of FLNa and FLNb in Th2 lymphocytes reduces airway inflammation through diminished Th2 lymphocyte recruitment in inflamed lungs. Collectively, our results highlight ASB2α and its substrates FLNa and FLNb to alter Th2 lymphocyte-mediated responses.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: A.S. is an employee of Sanofi. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Vieira Braga, F. A. et al. A cellular census of human lungs identifies novel cell states in health and in asthma. Nat. Med.25, 1153–1163 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Gandhi, N. A. et al. Targeting key proximal drivers of type 2 inflammation in disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov.15, 35–50 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Kolkhir, P. et al. Type 2 chronic inflammatory diseases: targets, therapies and unmet needs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov.22, 743–767 (2023). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

