Clinical and prognostic effects of microvascular density and FOXP3 positive T cells in breast cancer
- PMID: 39639042
- PMCID: PMC11621116
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-82106-2
Clinical and prognostic effects of microvascular density and FOXP3 positive T cells in breast cancer
Abstract
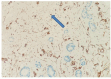
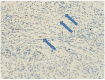
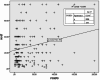
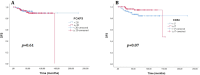
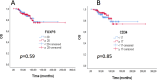
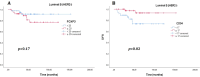
There are conflicting data regarding the prognostic effect of microvascular density (MVD) in breast cancer and its molecular subtypes. It is thought that high levels of FOXP3 + T cells in breast cancer are associated with poor prognosis. However, data regarding FOXP3 show significant variability in the literature. In our study, we aim to measure MVD and FOXP3 + T cells in breast cancer cases and investigate their relationship with each other and their effects on breast cancer patients' clinical and prognostic features. In our study, the results of 207 female breast cancer patients whose excisional tumoral tissue was obtained are presented. The study evaluated the findings under a light microscope using antibodies against CD34 for measuring MVD and FOXP3 for measuring FOXP3-positive T cells. CD34 ≥ 17 was categorized as high MVD, and CD34 < 17 was classified as low MVD. FOXP3 + cell count ≥ 20/mm2 was categorized as high FOXP3 positivity and < 20/mm2 as low FOXP3 positivity. The SPSS program (version 22) was used to evaluate the results statistically, and p < 0.05 was considered significant. The median age was 54.0 (27-86) years, and the median follow-up period was 60.0 (IQR: 42.6-86.5) months. In the high MVD group, a higher progesterone receptor (PR) positivity rate was detected (p = 0.035). High FOXP3 positivity was significantly associated with high nuclear grade (p = 0.003). High FOXP3 positivity was significantly associated with PR negativity and high Ki67 values (p = 0.009, p = 0.012, respectively). No statistically significant correlation was found between MVD elevation and FOXP3 positivity (r = 0.063, p = 0.36). A weakly significant positive correlation was detected between high Ki67 and FOXP3 positivity (r = 0.0146, p = 0.04). A weak inverse correlation was detected between high FOXP3 positivity and PR percentage values (r=-0.182, p = 0.01). While there was no significant difference in disease-free survival in cases with high MVD and high FOXP3 + T cells compared to groups with low levels, the results were not mature enough because the median values in overall survival could not be reached. A significant correlation was found between high FOXP3 positivity and some aggressive tumor features; no effect on survival was detected. In contrast to literature data on luminal A breast cancer, high MVD in the luminal B (HER2-) subgroup was associated with a lower risk of recurrence. Our study is the first in the literature to evaluate the relationship between MVD measured using CD34 and FOXP3 positive T cells in breast cancer. Our study found no correlation between MVD and FOXP3 positivity, while literature data show significant correlations in some other cancers.
Keywords: Breast cancer; CD34; FOXP3 T cells; Microvascular density.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Consent for publication: All authors have approved the manuscript and consented to publication.
Figures


References
-
- Uzzan, B., Nicolas, P., Cucherat, M. & Perret, G. Y. Microvessel Density as a prognostic factor in women with breast Cancer: a systematic review of the literature and Meta-analysis. Cancer Res.64, 2941–2955, May 1, 2004. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 20.GENEL.020/This study was supported by Afyonkarahisar Health Sciences University Scientific Research Projects Coordination
- 20.GENEL.020/This study was supported by Afyonkarahisar Health Sciences University Scientific Research Projects Coordination
- 20.GENEL.020/This study was supported by Afyonkarahisar Health Sciences University Scientific Research Projects Coordination
- 20.GENEL.020/This study was supported by Afyonkarahisar Health Sciences University Scientific Research Projects Coordination
- 20.GENEL.020/This study was supported by Afyonkarahisar Health Sciences University Scientific Research Projects Coordination
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

