Long term efficacy of first-line afatinib and the clinical utility of ctDNA monitoring in patients with suspected or confirmed EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer who were unsuitable for chemotherapy
- PMID: 39639088
- PMCID: PMC11790930
- DOI: 10.1038/s41416-024-02901-6
Long term efficacy of first-line afatinib and the clinical utility of ctDNA monitoring in patients with suspected or confirmed EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer who were unsuitable for chemotherapy
Abstract
Background: Here we present long-term outcomes of first line afatinib in comorbid patients with suspected or confirmed EGFR mutant NSCLC otherwise considered unsuitable for chemotherapy, and the clinical utility of serial ctDNA monitoring.
Methods: TIMELY (NCT01415011) was a multicentre, single arm, phase II trial conducted in the UK. Patients aged ≥18 were treated with daily oral afatinib (40 mg) until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Blood samples for ctDNA analysis were obtained at baseline and 12-weekly until treatment discontinuation. The primary endpoint was PFS.
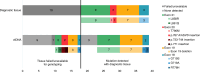
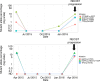
Results: Thirty-nine patients were enrolled between March 2013 and August 2015. Median follow-up was 98 months (range 69-101). Median PFS was 7.9 months (95% CI 4.6-10.5). Seven patients (18%) continued afatinib beyond 18 months, 3 beyond 36 months and 2 were still on treatment at last follow-up 101 months post-treatment initiation. Analysis of baseline ctDNA samples identified 8 EGFR mutant cases that were not identified by tissue genotyping and ctDNA clearance was associated with improved PFS and OS.
Conclusion: Afatinib is a viable treatment option for tissue or ctDNA-detected EGFR mutant NSCLC comorbid patients, with a proportion achieving long-term clinical benefit. Plasma ctDNA testing improved EGFR mutant identification and its clearance predicted improved PFS and OS.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Prof Popat’s has consulting /advisory Role with Amgen, AstraZeneca (AZ), Bayer, Blueprint, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS), Boehringer Ingelheim, Daiichi Sankyo, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), Guardant Health, Incyte, Janssen, Lilly, Merck Serono, Merck Sharp & Dohme (MSD), Novartis, Roche, Takeda, Pfizer, Seattle Genetics, Turning Point Therapeutics & EQRx. He has received payment/Honoraria from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Guardant Health, Janssen, Merck Serono, Roche & Takeda. He has provided expert testimony to Roche, Merck Serono. He has received meeting attendance support from Janssen & Roche. He has a leadership / fiduciary Role with the British Thoracic Oncology Group (BTOG), ALK Positive UK, Lung Cancer Europe, Ruth Strauss Foundation, Mesothelioma Applied Research Foundation & ETOP-IBCSG Partners Foundation Board. Dr Januszewski has received grant/holds contracts with Gilead & Roche. He has received teaching payments from AZ, Johnson and Johnson, Roche, Pfizer, MSD & Bayer. He has received meeting attendance support from Johnson & Johnson Pharmaceuticals & Roche Pharmaceuticals. He has an advisory role with BMS, AZ, Pfizer & MSD. He has a leadership/fiduciary role with BTOG. Dr Ahmad has received speaker payment from AZ. She has received payment for an advisory project from Roche and meeting attendance support from Takeda. Dr Shah has an advisory role with BI. He has received meeting attendance support from BI. He has a leadership / fiduciary role with BTOG & EGFR + UK. Dr Geldart has received honoraria from Merck and meeting attendance support from BMS. Prof Spicer has consulting compensation to author’s employer from AZ, BMS, GSK & RS Oncology; Advisory Board fees. He has an advisory role with CHM Cancer Vaccines Expert Working Group & CHM Expert Advisory Group on Oncology & Haematology. He has a leadership /fiduciary role with BTOG & Experimental Cancer Medicine Centres. He has stock/stock Options with Avacta & Epsiolgen. He has received reimbursements for treatment of trial patients from Achilles, BergenBio, BMS, Gilead, IO Biotech, Iovance, MSD, Roche, RS Oncology, Starpharma & Trizell. Dr Roitt has limited prior shares with Inivata. Dr Mulatero has stocks with Inivata. All remaining authors had no conflicts of interest to declare. Ethical approval and consent to participate: The TIMELY trial was approved by the Scotland A Research Ethics Committee. Written informed consent was obtained from all patients. The study was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Figures


References
-
- National Lung Cancer Audit annual report (for the audit period 2018) Version 2. London: Royal College of Physicians; 2021.
-
- Lee CK, Wu YL, Ding PN, Lord SJ, Inoue A, Zhou C, et al. Impact of Specific Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) mutations and clinical characteristics on outcomes after treatment with EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors versus chemotherapy in EGFR-mutant lung cancer: a meta-analysis. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33:1958–65. - PubMed
-
- Inoue A, Kobayashi K, Usui K, Maemondo M, Okinaga S, Mikami I, et al. First-line gefitinib for patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harboring epidermal growth factor receptor mutations without indication for chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:1394–1400. - PubMed
-
- Tsubata Y, Watanabe K, Saito R, Nakamura A, Yoshioka H, Morita M, et al. Osimertinib in poor performance status patients with T790M-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer after progression of first- and second-generation EGFR-TKI treatments (NEJ032B). Int J Clin Oncol. 2022;27:112–20. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Igawa S, Fukui T, Kasajima M, Ono T, Ozawa T, Kakegawa M, et al. First-line osimertinib for poor performance status patients with EGFR mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer: A prospective observational study. Invest N. Drugs. 2022;40:430–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

