Novel variants impairing Sp1 transcription factor binding in the COL7A1 promoter cause mild cases of recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa
- PMID: 39639148
- PMCID: PMC11894107
- DOI: 10.1038/s41431-024-01717-5
Novel variants impairing Sp1 transcription factor binding in the COL7A1 promoter cause mild cases of recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa
Abstract
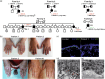
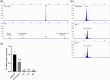
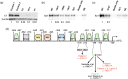
Recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (RDEB) is a rare and most often severe genodermatosis characterized by recurrent blistering and erosions of the skin and mucous membranes after minor trauma, leading to major local and systemic complications. RDEB is caused by loss-of-function mutations in COL7A1 encoding type VII collagen (C7), the main component of anchoring fibrils which form attachment structures stabilizing the cutaneous basement membrane zone. Most of the previously reported COL7A1 mutations are located in the coding or intronic regions. We describe 6 patients with localized or intermediate RDEB for whom one recessive pathogenic variant in the coding region and a second variant in the COL7A1 promoter were identified. These substitutions, three of which are novel, are localized in two Sp1 binding sites of the promoter region. DNA pull-down assay showed a drastic reduction of Sp1 binding consistent with a dramatic decrease in COL7A1 transcript and almost undetectable C7 protein levels. Our results reveal that mutations in the COL7A1 promoter on the background of a null allele can underlie localized or intermediate RDEB. They further emphasize the functional importance of Sp1 motifs in the proximal COL7A1 promoter which should be carefully investigated for regulatory mutations in the case of RDEB with only one pathogenic variant identified in the coding or intronic regions.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval and consent to participate: The samples were obtained with appropriate informed consent from all participants in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. Informed consents were obtained from the individuals and/or legal guardians, including permission for the publication of clinical photographs and details.
Figures
References
-
- Has C, Bauer JW, Bodemer C, Bolling MC, Bruckner‐Tuderman L, Diem A, et al. Consensus reclassification of inherited epidermolysis bullosa and other disorders with skin fragility. Br J Dermatol. 2020;183:614–27. 10.1111/bjd.18921. - PubMed
-
- Gardella R, Barlati S, Zoppi N, Tadini G, Colombi M. A -96C>T mutation in the promoter of the collagen type VII gene (COL7A1) abolishing transcription in a patient affected by recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Hum Mutat. 2000;16:275. - PubMed
-
- Gardella R, Zoppi N, Ferraboli S, Marini D, Tadini G, Barlati S, et al. Three homozygous PTC mutations in the collagen type VII gene of patients affected by recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa: analysis of transcript levels in dermal fibroblasts. Hum Mutat. 1999;13:439–52. - PubMed
-
- Ritelli M, Chiarelli N, Quinzani S, Dordoni C, Venturini M, Calzavara-Pinton P, et al. Compound heterozygosity of the novel −186C>T mutation in the COL7A1 promoter and the recurrent c.497insA mutation leads to generalized dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa: correspondence. Br J Dermatol. 2013;168:904–6. 10.1111/bjd.12063. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

