Cell Painting: a decade of discovery and innovation in cellular imaging
- PMID: 39639168
- PMCID: PMC11810604
- DOI: 10.1038/s41592-024-02528-8
Cell Painting: a decade of discovery and innovation in cellular imaging
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Cell Painting: a decade of discovery and innovation in cellular imaging.Nat Methods. 2025 Feb;22(2):447. doi: 10.1038/s41592-024-02578-y. Nat Methods. 2025. PMID: 39668211 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
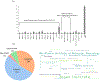
Modern quantitative image analysis techniques have enabled high-throughput, high-content imaging experiments. Image-based profiling leverages the rich information in images to identify similarities or differences among biological samples, rather than measuring a few features, as in high-content screening. Here, we review a decade of advancements and applications of Cell Painting, a microscopy-based cell-labeling assay aiming to capture a cell's state, introduced in 2013 to optimize and standardize image-based profiling. Cell Painting's ability to capture cellular responses to various perturbations has expanded owing to improvements in the protocol, adaptations for different perturbations, and enhanced methodologies for feature extraction, quality control, and batch-effect correction. Cell Painting is a versatile tool that has been used in various applications, alone or with other -omics data, to decipher the mechanism of action of a compound, its toxicity profile, and other biological effects. Future advances will likely involve computational and experimental techniques, new publicly available datasets, and integration with other high-content data types.
© 2024. Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: S. Singh and A.E.C. serve as scientific advisors for companies that use image-based profiling and Cell Painting (A.E.C.: Recursion, SyzOnc, Quiver Bioscience; S. Singh: Waypoint Bio, Dewpoint Therapeutics, DeepCell) and receive honoraria for occasional talks at pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies. J.C.P. and O.S. declare ownership in Phenaros Pharmaceuticals. M.-A.T. and N.G. were formerly employed at AstraZeneca. M.-A.T. and N.G. are currently employed at Recursion Pharmaceuticals. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

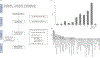
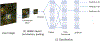
References
-
- Swinney DC & Anthony J How were new medicines discovered? Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 2011 10:7 10, 507–519 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Moffat JG, Vincent F, Lee JA, Eder J & Prunotto M Opportunities and challenges in phenotypic drug discovery: an industry perspective. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 2017 16:8 16, 531–543 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Perlman ZE et al. Multidimensional drug profiling by automated microscopy. Science (1979) 306, 1194–1198 (2004). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

