Aromadendrin Ameliorates Airway Inflammation in Experimental Mice with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- PMID: 39639498
- PMCID: PMC11813338
- DOI: 10.4014/jmb.2408.08022
Aromadendrin Ameliorates Airway Inflammation in Experimental Mice with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Abstract
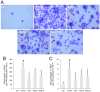
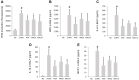
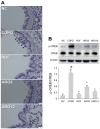
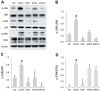
Aromadendrin (ARO) is an active plant compound that exerts anti-inflammatory effects. However, its ameliorative effects on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) remain unclear. Therefore, we investigated the inhibitory effects of ARO on bronchial inflammation using an experimental model of COPD. In vivo analysis confirmed a notable increase in the number of neutrophils/macrophages and the formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), myeloperoxidase (MPO), interleukin (IL)-6/IL-1β, and monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)-1 in the bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid of COPD mice, which was attenuated by oral gavage of ARO. In addition, hematoxylin and eosin staining showed a notable cell influx in the lungs of the COPD group, which was ameliorated by ARO. Western blotting revealed that ARO decreased the upregulation of neutrophil elastase expression in the lungs of the COPD group. Furthermore, periodic acid-Schiff staining showed that increased mucus formation in the lungs of the COPD group was downregulated by ARO. ARO also blocked CREB activation in the lungs of COPD mice. This in vivo, anti-inflammatory effect of ARO was accompanied by its modulatory effect on the activation of the MAPK/NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome. In summary, our study demonstrated that ARO has protective effects on bronchial inflammation by attenuating immune cell accumulation, toxic molecule/cytokine/chemokine formation, and MAPK/NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome activation, suggesting the potential development of ARO as an adjuvant for the prevention and treatment of COPD.
Keywords: COPD; NF-κB; NLRP3 inflammasome; aromadendrin; cytokines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
3,4,5-Trihydroxycinnamic acid exerts a protective effect on pulmonary inflammation in an experimental animal model of COPD.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Aug;85:106656. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106656. Epub 2020 Jun 5. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32504994
-
Aromadendrin inhibits PMA-induced cytokine formation/NF-κB activation in A549 cells and ovalbumin-induced bronchial inflammation in mice.Heliyon. 2023 Nov 26;9(12):e22932. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e22932. eCollection 2023 Dec. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38125474 Free PMC article.
-
The anti-inflammatory effect of BML-111 on COPD may be mediated by regulating NLRP3 inflammasome activation and ROS production.Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2018 Sep;138:23-30. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2018.08.001. Epub 2018 Aug 10. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2018. PMID: 30102962
-
Carbenoxolone Ameliorates Allergic Airway Inflammation through NF-κB/NLRP3 Pathway in Mice.Biol Pharm Bull. 2022 Jun 1;45(6):743-750. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b21-01100. Epub 2022 Apr 15. Biol Pharm Bull. 2022. PMID: 35431287
-
Andrographolide ameliorates OVA-induced lung injury in mice by suppressing ROS-mediated NF-κB signaling and NLRP3 inflammasome activation.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 6;7(49):80262-80274. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12918. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27793052 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

