PanicleNeRF: Low-Cost, High-Precision In-Field Phenotyping of Rice Panicles with Smartphone
- PMID: 39639877
- PMCID: PMC11617619
- DOI: 10.34133/plantphenomics.0279
PanicleNeRF: Low-Cost, High-Precision In-Field Phenotyping of Rice Panicles with Smartphone
Abstract
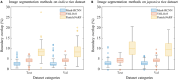
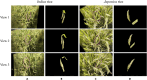
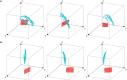
The rice panicle traits substantially influence grain yield, making them a primary target for rice phenotyping studies. However, most existing techniques are limited to controlled indoor environments and have difficulty in capturing the rice panicle traits under natural growth conditions. Here, we developed PanicleNeRF, a novel method that enables high-precision and low-cost reconstruction of rice panicle three-dimensional (3D) models in the field based on the video acquired by the smartphone. The proposed method combined the large model Segment Anything Model (SAM) and the small model You Only Look Once version 8 (YOLOv8) to achieve high-precision segmentation of rice panicle images. The neural radiance fields (NeRF) technique was then employed for 3D reconstruction using the images with 2D segmentation. Finally, the resulting point clouds are processed to successfully extract panicle traits. The results show that PanicleNeRF effectively addressed the 2D image segmentation task, achieving a mean F1 score of 86.9% and a mean Intersection over Union (IoU) of 79.8%, with nearly double the boundary overlap (BO) performance compared to YOLOv8. As for point cloud quality, PanicleNeRF significantly outperformed traditional SfM-MVS (structure-from-motion and multi-view stereo) methods, such as COLMAP and Metashape. The panicle length was then accurately extracted with the rRMSE of 2.94% for indica and 1.75% for japonica rice. The panicle volume estimated from 3D point clouds strongly correlated with the grain number (R 2 = 0.85 for indica and 0.82 for japonica) and grain mass (0.80 for indica and 0.76 for japonica). This method provides a low-cost solution for high-throughput in-field phenotyping of rice panicles, accelerating the efficiency of rice breeding.
Copyright © 2024 Xin Yang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures







References
-
- He X, Batáry P, Zou Y, Zhou W, Wang G, Liu Z, Bai Y, Gong S, Zhu Z, Settele J, et al. . Agricultural diversification promotes sustainable and resilient global rice production. Nat Food. 2023;4(9):788–796. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

