Long-Term clinical efficacy of liraglutide for type 2 diabetes: real-world evidence and outcomes from Pakistan
- PMID: 39640418
- PMCID: PMC11619037
- DOI: 10.1080/20523211.2024.2432462
Long-Term clinical efficacy of liraglutide for type 2 diabetes: real-world evidence and outcomes from Pakistan
Abstract
Background: Liraglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, has demonstrated efficacy in improving glycemic control and promoting weight loss in clinical trials. However, real-world data from diverse populations, particularly from South Asia, are limited. The study aims to evaluate the long-term efficacy and safety of liraglutide in a real-world setting among Pakistani patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
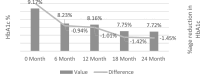
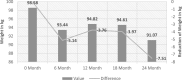
Methodology: A retrospective cohort study of 624 patients initiated on liraglutide was conducted. Data were collected at baseline and 6, 12, 18, and 24 months. Primary outcomes were HbA1c and weight changes. Secondary outcomes included fasting plasma glucose, lipid profile, and blood pressure. Statistical analyses were performed using appropriate methods.
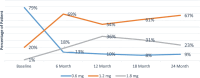
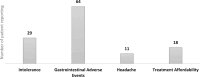
Results: In study population the mean HbA1c reduction of -1.45 ± 0.67% was observed at 24 months, with 30.6% achieving HbA1c ≤ 7.5%. A rapid and sustained weight loss of -7.51 kg was achieved, with 27.2% experiencing ≥5% weight loss. Additionally, liraglutide led to a significant reduction in LDL cholesterol, with 46.7% of patients achieving a ≥ 10% reduction at 24 months. Liraglutide was well-tolerated, with a low discontinuation rate of 4.6%.
Conclusion: Liraglutide demonstrated sustained efficacy and safety in a diverse Pakistani population with T2DM, regardless of baseline characteristics. These findings support the use of liraglutide as an effective treatment option for T2DM in real-world clinical practice.
Keywords: Glucagon-like peptide (GLP-1); clinical effectiveness; diabetes mellitus type 2; glycemic control; real-world data.
© 2024 The Author(s). Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Berra, C., Manfrini, R., Regazzoli, D., Radaelli, M., Disoteo, O., Sommese, C., … Folli, F. (2020). Blood pressure control in type 2 diabetes mellitus with arterial hypertension. The important ancillary role of SGLT2-inhibitors and GLP1-receptor agonists. Pharmacological Research, 160, 105052. 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105052 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources