MRI Denoising Using Pixel-Wise Threshold Selection
- PMID: 39640512
- PMCID: PMC11619618
- DOI: 10.1109/access.2024.3449811
MRI Denoising Using Pixel-Wise Threshold Selection
Abstract
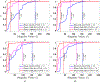
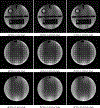
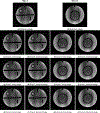
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has emerged as a promising technique for non-invasive medical imaging. The primary challenge in MRI is the trade-off between image visual quality and acquisition time. Current MRI image denoising algorithms employ global thresholding to denoise the whole image, which leads to inadequate denoising or image distortion. This study introduces a novel pixel-wise (localized) thresholding approach of singular vectors, obtained from singular value decomposition, to denoise magnetic resonance (MR) images. The pixel-wise thresholding of singular vectors is performed using separate singular values as thresholds at each pixel, which is advantageous given the spatial noise variation throughout the image. The method presented is validated on MR images of a standard phantom approved by the magnetic resonance accreditation program (MRAP). The denoised images display superior visual quality and recover minute structural information otherwise suppressed in the noisy image. The increase in peak-signal-to-noise-ratio (PSNR) and contrast-to-noise-ratio (CNR) values of ≥ 18% and ≥ 200% of the denoised images, respectively, imply efficient noise removal and visual quality enhancement. The structural similarity index (SSIM) of ≥ 0.95 for denoised images indicates that the crucial structural information is recovered through the presented method. A comparison with the standard filtering methods widely used for MRI denoising establishes the superior performance of the presented method. The presented pixel-wise denoising technique reduces the scan time by 2-3 times and has the potential to be integrated into any MRI system to obtain faster and better quality images.
Keywords: Magnetic resonance imaging; SF-SVD; contrast-to-noise ratio; denoising; image denoising; peak-signal-to-noise ratio; pixel-wise noise threshold selection; pixel-wise thresholding; singular value decomposition; structural similarity index.
Figures

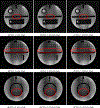
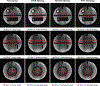

References
-
- Mohan J, Krishnaveni V, and Guo Y, “A survey on the magnetic resonance image denoising methods,” Biomed. Signal Process. Control, vol. 9, pp. 56–69, Jan. 2014.
-
- Mohsen YM, Abdelghany HS, and Saleh RN, “Advanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technique (double inversion recovery sequence) in the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis (MS) grey matter lesions,” Minia J. Med. Res, vol. 34, no. 1, pp. 65–75, 2023.
-
- Henkelman RM, “Measurement of signal intensities in the presence of noise in MR images,” Med. Phys, vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 232–233, Mar. 1985. - PubMed
-
- Dietrich O, Raya JG, Reeder SB, Reiser MF, and Schoenberg SO, “Measurement of signal-to-noise ratios in MR images: Influence of multichannel coils, parallel imaging, and reconstruction filters,” J. Magn. Reson. Imag, vol. 26, no. 2, pp. 375–385, Aug. 2007. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
