Berbamine prevents SARS-CoV-2 entry and transmission
- PMID: 39640591
- PMCID: PMC11618033
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.111347
Berbamine prevents SARS-CoV-2 entry and transmission
Abstract
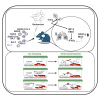
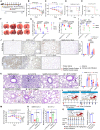
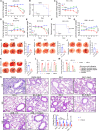
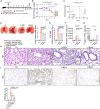
Effective antiviral drugs are essential to combat COVID-19 and future pandemics. Although many compounds show antiviral in vitro activity, only a few retain effectiveness in vivo against SARS-CoV-2. Here, we show that berbamine (Berb) is effective against SARS-CoV, MER-CoV, SARS-CoV-2 and its variants, including the XBB.1.16 variant. In hACE2.Tg mice, Berb suppresses SARS-CoV-2 replication through two distinct mechanisms: inhibiting spike-mediated viral entry and enhancing antiviral gene expression during infection. The administration of Berb, in combination with remdesivir (RDV), clofazimine (Clof) and fangchinoline (Fcn), nearly eliminated viral load and promoted recovery from acute SARS-CoV-2 infection and its variants. Co-housed mice in direct contact with either pre-treated or untreated infected mice exhibited negligible viral loads, reduced lung pathology, and decreased viral shedding, suggesting that Berb may effectively hinder virus transmission. This broad-spectrum activity positions Berb as a promising preventive or therapeutic option against betacoronaviruses.
Keywords: drugs; health sciences; virology.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors read the manuscript and declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Gorbalenya A.E., Baker S.C., Baric R.S., De Groot R., Drosten C., Gulyaeva A.A., Haagmans B., Lauber C., Leontovich A.M., Neuman B.W., et al. The species Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: classifying 2019-nCoV and naming it SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Microbiol. 2020;5:536–544. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

