Plant-mediated synthesis of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles using Alnus nepalensis D. Don for biological applications
- PMID: 39640779
- PMCID: PMC11620262
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39255
Plant-mediated synthesis of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles using Alnus nepalensis D. Don for biological applications
Abstract
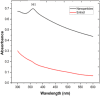
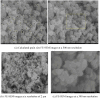
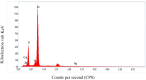
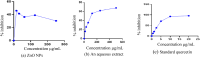
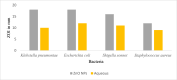
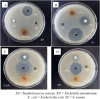
An aqueous bark extract of A. nepalensis D. Don was utilized to prepare zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles through a green method, which is more economical, eco-friendly, and effective for exploring several biological applications and toxicity assessments against brine shrimp nauplii. The prepared ZnO nanoparticles were characterized using several characterizing techniques. The surface morphology and the elemental composition of the prepared ZnO NPs was analyzed by field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), and energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) analysis. The colour of the solution was changed from reddish-brown to white indicating the formation of ZnO NPs which shows UV-vis absorption at 361 nm. The various functional groups of the organic compounds present in plant extract act as reducing and stabilizing agents in the formation of nanoparticles. The involvement of these functionalities in the formation of nanoparticles is indicated by the shifts and changes in the IR spectra of both the plant extract and the ZnO nanoparticles. The size of the nanoparticles was determined to be 15.31 nm with XRD analysis while the FE-SEM revealed the average grain size of 67.29 nm with irregular shape. The elemental composition of ZnO NPs shows a greater atomic percentage of zinc compared to other elements (C, N, Ni, O, and Ag), with an intense peak of zinc observed at approximately 1 keV. The trace amount of silver is due to the impurities present in the reagent used in the experiment. The antioxidant property of ZnO nanoparticles was evaluated with an IC₅₀ of 53.02 ± 3.43 μg/mL. The ZnO nanoparticles exhibited significant antibacterial activity against Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli, with zones of inhibition (ZOI) of 18 mm and 23 mm, respectively as compared to the positive control neomycin of ZOI 28 mm against K. pneumoniae. The potential antibacterial activity of the ZnO NPS was revealed as the MIC and MBC against K. pneumoniae of 0.39 mg/mL and 0.78 mg/mL, respectively. In addition, the prepared ZnO nanoparticles showed toxicity against brine shrimp nauplii of LC₅₀ 16.59 μg/mL. The results of this study impart that plant-assisted synthesized ZnO nanoparticles possess significant antibacterial properties that reduce oxidative stress in human cells, ultimately contributing to cancer prevention.
Keywords: Alnus nepalensis D. Don; Antimicrobial; Antioxidant; Green synthesis; MBC; MIC; Toxicity; Zinc oxide nanoparticles.
© 2024 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests:Khaga Raj Sharma reports financial support was provided by 10.13039/501100009647University Grants Commission. Khaga raj Sharma reports a relationship with 10.13039/501100009647University Grants Commission that includes: funding grants. Khaga Raj Sharma has patent Not pending to Not. Not any financial support from other institutions support If there are other authors, they declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures










References
-
- Xia C., Zhao W., Wang J., Sun J., Cui G., Zhang L. Progress on geographical distribution, driving factors and ecological functions of Nepalese alder. Diversity. 2023;15(1):59. doi: 10.3390/d15010059. - DOI
-
- Nadeem M., Tungmunnithum D., Hano C., Abbasi B.H., Hashmi S.S., Ahmad W., Zahir A. The current trends in the green syntheses of titanium oxide nanoparticles and their applications. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2018;11(4):492–502. doi: 10.1080/17518253.2018.1538430. - DOI
-
- Gul R., Jan H., Lalay G., Andleeb A., Usman H., Zainab R., Qamar Z., Hano C., Abbasi B.H. Medicinal plants and biogenic metal oxide nanoparticles: a paradigm shift to treat Alzheimer's disease. Coatings. 2021;11(6):717. doi: 10.3390/coatings11060717. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

