Locus coeruleus tau is linked to successive cortical tau accumulation
- PMID: 39641328
- PMCID: PMC11848382
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.14426
Locus coeruleus tau is linked to successive cortical tau accumulation
Abstract
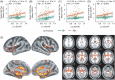
Introduction: We investigated the hypothesis that tau burden in the locus coeruleus (LC) correlates with tau accumulation in cortical regions according to the Braak stages and examined whether the relationships differed according to cortical amyloid beta (Aβ) deposition.
Methods: One hundred and seventy well-characterized participants from an ongoing cohort were included. High-resolution T1, tau positron emission tomography (PET), and amyloid PET were obtained.
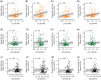
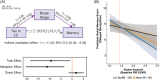
Results: LC tau burden was significantly linked to global tau in neocortical regions, as was tau in both early Braak stage (stage I/II) and later Braak stage areas. This relationship was significant only in Aβ-positive individuals. While LC tau did not directly impact memory, it was indirectly associated with delayed memory through mediation or moderation pathways.
Discussion: The findings from living human brains support the idea that LC tau closely relates to subsequent cortical tau accumulation, particularly among individuals with pathological Aβ accumulation, and identify LC tau burden as a promising indicator of cognitive trajectories of AD.
Highlights: Tau burden in the LC was significantly associated with cortical tau accumulation. Tau burden in SN or PPN showed no association with cortical tau accumulation. LC tau burden was serially associated with Braak stages. The tau-LC and cortical tau relationship was significant only in the Aβ-positive group. Cortical amyloid's impact on memory worsens with higher tau accumulation in the LC.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; amyloid beta; cortical tau accumulation; locus coeruleus; tau pathology.
© 2024 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Saykin receives support from multiple NIH grants (P30 AG010133, P30 AG072976, R01 AG019771, R01 AG057739, U19 AG024904, R01 LM013463, R01 AG068193, T32 AG071444, U01 AG068057, U01 AG072177, and U19 AG074879). He has also received support from Avid Radiopharmaceuticals, a subsidiary of Eli Lilly (in kind contribution of PET tracer precursor) and participated in scientific advisory boards (Bayer Oncology, Eisai, Novo Nordisk, and Siemens Medical Solutions USA, Inc.) and an Observational Study Monitoring Board (MESA, NIH NHLBI), as well as external advisory committees for multiple NIA grants. He also serves as editor‐in‐chief of
Figures

References
-
- Braak H, Braak E. Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer‐related changes. Acta Neuropathol. 1991;82:239‐259. - PubMed
-
- Braak H, Thal DR, Ghebremedhin E, Del Tredici K. Stages of the pathologic process in Alzheimer disease: age categories from 1 to 100 years. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2011;70:960‐969. - PubMed
-
- Braak H, Del Tredici K. The pathological process underlying Alzheimer's disease in individuals under thirty. Acta Neuropathol. 2011;121:171‐181. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AG019771/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG068193/National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R37 AG057739/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG068057/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HI18C0630/Korean government
- RS-2023-KH136195/New Faculty Startup Fund from Seoul National University
- U19AG024904/National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01AG057739/National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- U01AG068057/National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- P30AG010133/National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 LM013463/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AG071444/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01668AG019771/National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- U01 AG072177/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AG074879/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NRF-2014M3C7A1046042/Korean government
- P30AG072976/National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- U19 AG024904/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01AG072177/National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- U19AG074879/National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- T32AG071444/National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01LM013463/National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- RS-2022-00165636/New Faculty Startup Fund from Seoul National University
- R01 AG057739/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG068193/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072976/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HI19C0149/Korean government
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

