The POINTER Imaging baseline cohort: Associations between multimodal neuroimaging biomarkers, cardiovascular health, and cognition
- PMID: 39641363
- PMCID: PMC11772730
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.14399
The POINTER Imaging baseline cohort: Associations between multimodal neuroimaging biomarkers, cardiovascular health, and cognition
Abstract
Introduction: The U.S. Study to Protect Brain Health Through Lifestyle Intervention to Reduce Risk (U.S. POINTER) is evaluating lifestyle interventions in older adults at risk for cognitive decline and dementia. Here we characterize the baseline data set of the POINTER Imaging ancillary study.
Methods: Participants underwent health and cognitive assessments and neuroimaging with multimodal positron emission tomography (PET) (beta-amyloid [Aβ] and tau) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Framingham risk score (FRS) was used to quantify cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk.
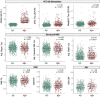
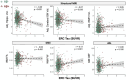
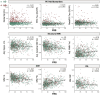
Results: A total of 1052 participants (31% from underrepresented ethnoracial groups) were enrolled. Compared to Aβ-, Aβ+ (29%) participants were older, had higher apolipoprotein E (APOE) ε4 carriage rate and white matter hyperintensity volume, and greater temporal tau. FRS was related to MRI measures, but not AD biomarkers. FRS and tau had independent effects on cognition.
Discussion: In this heterogenous, at-risk cohort, CVD risk was related to more abnormal brain structure and poorer cognition, representing a putative non-AD (Alzheimer's disease) pathway to brain injury and cognitive decline.
Highlights: ·The U.S. Study to Protect Brain Health Through Lifestyle Intervention to Reduce Risk (U.S. POINTER) cohort is enriched for cardiovascular disease (CVD) and poor lifestyle ·POINTER Imaging collected multimodal neuroimaging data in this unique, at-risk cohort ·Amyloid burden was related to age, apolipoprotein E (APOE) ε4 carriage, and measures of disease progression ·Associations between amyloid and tau, and tau and cognition, were relatively weak ·CVD risk and tau pathology were independently related to memory.
Keywords: Framingham risk score; MRI; PET; amyloid; cerebrovascular injury; memory; minoritized groups; preclinical Alzheimer's disease; tau.
© 2024 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Theresa M. Harrison, Tyler Ward, Jacinda Taggett, Pauline Maillard, Youngkyoo Jung, Laura C. Lovato, Robert Koeppe, Neelum T. Aggarwal, Mark A. Espeland, Maryjo L. Cleveland, Rachel Whitmer, Sarah Tomaszewski Farias, Valory Pavlik, Melissa Yu, Christine Tangney, Laura D. Baker, and Prashanthi Vemuri have no potential conflicts to report. Samuel N. Lockhart: National Institutes of Health (NIH) and Alzheimer's Association grants to the institution; has served on the Data Safety and Monitoring Board (DSMB for the WALL‐e study (NCT04908358). Danielle Harvey: serves as a statistical advisor for PLOS ONE, and has served as a consultant for NervGen Pharma Corp. William J. Jagust: consults for Lilly, Eisai, and Prothena. Joseph C. Masdeu: consults for Lilly. Hwamee Oh: serves on the DSMB for the NIH‐funded study at MGH. Darren R. Gitelman: Consults for Abbvie, Novo Nordisk, Nutricia, and WIRB‐Copernicus; speaking honorarium for Eisai; research contracts with Biogen, Cassava, Eisai, and Lilly; and travel support from the Alzheimer's Association, Eisai, and the Global Alzheimer's Platform. Stephen Salloway: Received grant funding from Lilly, Biogen, Genentech, Roche, Eisai, and Novartis, and has received consulting and/or travel fees from Lilly, Biogen, Roche, Genentech, Eisai, NovoNordisk, Prothena, AbbVie, Acumen, CognitionRX, and Kisbee; in addition, he has received support for serving as Project Arm Leader for the DIAN‐TU study. Heather Snyder: is a full‐time employee of the Alzheimer's Association; her spouse works for Abbott Labs in an unrelated field. Maria Carrillo: is a full‐time employee of the Alzheimer's Association. Charles DeCarli: consults for Eisai and Nova Nordisk. Susan M. Landau: has received speaking honoraria from Eisai and IMPACT AD, has served on the DSMB for KeifeRx and the NIH Impact of Intensive Treatment of Systolic Blood Pressure on Brain Perfusion, Amyloid and Tau in Older Adults (IPAT) study, has consulted for Banner Health and has received research support from the Alzheimer's Association. Author disclosures are available in the Supporting Information.
Figures

References
-
- Whitmer RA, Baker LD, Carrillo MC, et al. Baseline Characteristics of the U.S. Study to Protect Brain Health through Lifestyle Intervention to Reduce Risk (U.S. POINTER): Successful Enrollment of a Diverse Clinical Trial Cohort at Risk for Cognitive Decline. Alzheimer's and Dementia. (In Press).
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

